Shotgun Metagenomics Reveals Taxonomic and Functional Shifts in Hot Water Microbiome Due to Temperature Setting and Stagnation
- PMID: 30542327
- PMCID: PMC6277882
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02695
Shotgun Metagenomics Reveals Taxonomic and Functional Shifts in Hot Water Microbiome Due to Temperature Setting and Stagnation
Abstract
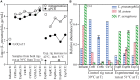
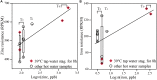
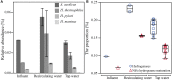
Hot water premise plumbing has emerged as a critical nexus of energy, water, and public health. The composition of hot water microbiomes is of special interest given daily human exposure to resident flora, especially opportunistic pathogens (OPs), which rely on complex microbial ecological interactions for their proliferation. Here, we applied shotgun metagenomic sequencing to characterize taxonomic and functional shifts in microbiomes as a function of water heater temperature setting, stagnation in distal pipes, and associated shifts in water chemistry. A cross-section of samples from controlled, replicated, pilot-scale hot water plumbing rigs representing different temperature settings (39, 42, and 51°C), stagnation periods (8 h vs. 7 days), and time-points, were analyzed. Temperature setting exhibited an overarching impact on taxonomic and functional gene composition. Further, distinct taxa were selectively enriched by specific temperature settings (e.g., Legionella at 39°C vs. Deinococcus at 51°C), while relative abundances of genes encoding corresponding cellular functions were highly consistent with expectations based on the taxa driving these shifts. Stagnation in distal taps diminished taxonomic and functional differences induced by heating the cold influent water to hot water in recirculating line. In distal taps relative to recirculating hot water, reads annotated as being involved in metabolism and growth decreased, while annotations corresponding to stress response (e.g., virulence disease and defense, and specifically antibiotic resistance) increased. Reads corresponding to OPs were readily identified by metagenomic analysis, with L. pneumophila reads in particular correlating remarkably well with gene copy numbers measured by quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Positive correlations between L. pneumophila reads and those of known protozoan hosts were also identified. Elevated proportions of genes encoding metal resistance and hydrogen metabolism were noted, which was consistent with elevated corrosion-induced metal concentrations and hydrogen generation. This study provided new insights into real-world factors influencing taxonomic and functional compositions of hot water microbiomes. Here metagenomics is demonstrated as an effective tool for screening for potential presence, and even quantities, of pathogens, while also providing diagnostic capabilities for assessing functional responses of microbiomes to various operational conditions. These findings can aid in informing future monitoring and intentional control of hot water microbiomes.
Keywords: Legionella; drinking water; hydrogen metabolism; metagenome; metal resistance; microbiome; opportunistic pathogens; premise plumbing.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Interactive effects of temperature, organic carbon, and pipe material on microbiota composition and Legionella pneumophila in hot water plumbing systems.Microbiome. 2017 Oct 4;5(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s40168-017-0348-5. Microbiome. 2017. PMID: 28978350 Free PMC article.
-
Shotgun Metagenomics Reveals Impacts of Copper and Water Heater Anodes on Pathogens and Microbiomes in Hot Water Plumbing Systems.Environ Sci Technol. 2023 Sep 12;57(36):13612-13624. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.3c03568. Epub 2023 Aug 29. Environ Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 37643149 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of heat shock on hot water plumbing microbiota and Legionella pneumophila control.Microbiome. 2018 Feb 9;6(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0406-7. Microbiome. 2018. PMID: 29426363 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Review: Propensity of Premise Plumbing Pipe Materials to Enhance or Diminish Growth of Legionella and Other Opportunistic Pathogens.Pathogens. 2020 Nov 17;9(11):957. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9110957. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 33212943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Required water temperature in hotel plumbing to control Legionella growth.Water Res. 2020 Sep 1;182:115943. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115943. Epub 2020 May 22. Water Res. 2020. PMID: 32590203
Cited by
-
Diverse and active archaea communities occur in non-disinfected drinking water systems-Less activity revealed in disinfected and hot water systems.Water Res X. 2021 Apr 27;12:100101. doi: 10.1016/j.wroa.2021.100101. eCollection 2021 Aug 1. Water Res X. 2021. PMID: 34027378 Free PMC article.
-
Credibility assessment of cold adaptive Pseudomonas jesenni MP1 and P. palleroniana N26 on growth, rhizosphere dynamics, nutrient status, and yield of the kidney bean cultivated in Indian Central Himalaya.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jan 30;14:1042053. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1042053. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36798715 Free PMC article.
-
Active eukaryotes in drinking water distribution systems of ground and surface waterworks.Microbiome. 2019 Jul 3;7(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s40168-019-0715-5. Microbiome. 2019. PMID: 31269979 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial risks in drinking water systems: persistence and public health implications of opportunistic premise plumbing pathogens.Front Microbiol. 2025 May 8;16:1575789. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1575789. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40406344 Free PMC article.
-
Tap water as a natural vehicle for microorganisms shaping the human gut microbiome.Environ Microbiol. 2022 Sep;24(9):3912-3923. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.15988. Epub 2022 Apr 7. Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35355372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alawadhi N., Egli T., Hamer G., Wehrli E. (1989). Thermotolerant and thermophilic solvent-utilizing methylotrophic, aerobic-bacteria. Systemat. Appl. Microbiol. 11 207–216. 10.1016/S0723-2020(89)80063-3 - DOI
-
- Andrei M., di Gabriele F., Bonora P. L., Scantlebury D. (2003). Corrosion behaviour of magnesium sacrificial anodes in tap water. Mater. Corrosion-Werkstoffe Korros. 54 5–11. 10.1002/maco.200390010 - DOI
-
- ARICO Plumbing Heating Cooling (2015). The Water Heater Anode Rod. Available at: https://www.aricoplumbing.com/waterheater-anode-rods [accessed June 1 2018].
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

