Interactions of Aspergillus fumigatus and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in an in vitro Mixed Biofilm Model: Does the Strain Matter?
- PMID: 30542331
- PMCID: PMC6277776
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02850
Interactions of Aspergillus fumigatus and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in an in vitro Mixed Biofilm Model: Does the Strain Matter?
Abstract
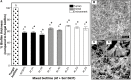
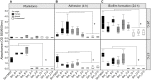
Introduction: Aspergillus fumigatus (Af) and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (Sm) are pathogenic microorganisms, which coexist in the respiratory tract of cystic fibrosis (CF) patients. We recently developed an in vitro model of mixed biofilm associating Af ATCC 13073-GFP (Af13073) and Sm ATCC 13637 (Sm13637) and described an antibiosis effect. The present study aim was to assess the antibiosis of Sm on Af using different strains and to analyze the potential synergistic virulence of these strains in an in vivo Galleria mellonella model. Methods: The effect of Sm13637 was evaluated on eight Af strains and the effect of nine Sm strains was evaluated on Af13073. The strains originated from clinical cases (human and animal) and from environment. Fungal and bacterial inocula were simultaneously inoculated to initiate mixed biofilm formation. Fungal growth inhibition was analyzed by qPCR and CLSM and the fungal cell wall modifications by TEM analysis. The virulence of different Sm strains was assessed in association with Af in G. mellonella larvae. Results: All strains of Af and Sm were able to produce single and mixed biofilms. The antibiosis effect of Sm13637 was similar whatever the Af strain tested. On the other hand, the antibiosis effect of Sm strains was bacterial-fitness and strain dependent. One strain (1/9) originated from animal clinical case was never able to induce an antibiosis, even with high bacterial concentration. In the G. mellonella model, co-inoculation with Sm13637 and Af13073 showed synergism since the mortality was 50%, i.e., more than the summed virulence of both. Conclusion: Human clinical strains of Sm yielded in higher antibiosis effect on Af and in a thinner mixed biofilm, probably due to an adaptive effect of these strains. Further research covering Af increased wall thickness in the presence of Sm strains, and its correlation with modified antifungal susceptibility is encouraged in patients with chronic respiratory infections by these 2 microorganisms.
Keywords: Aspergillus fumigatus; Galleria mellonella; Stenotrophomonas maltophilia; antibiosis; bacterial-fungal interactions; mixed biofilm.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Modulated Response of Aspergillus fumigatus and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia to Antimicrobial Agents in Polymicrobial Biofilm.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Oct 6;10:574028. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.574028. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33123497 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of Aspergillus fumigatus in Association with Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in an In Vitro Model of Mixed Biofilm.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 21;11(11):e0166325. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166325. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27870863 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiosis interaction of Staphylococccus aureus on Aspergillus fumigatus assessed in vitro by mixed biofilm formation.BMC Microbiol. 2015 Feb 15;15:33. doi: 10.1186/s12866-015-0363-2. BMC Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25880740 Free PMC article.
-
Secondary Metabolites Produced during Aspergillus fumigatus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Formation.mBio. 2022 Aug 30;13(4):e0185022. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01850-22. Epub 2022 Jul 20. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35856657 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between Bacteria and Aspergillus fumigatus in Airways: From the Mycobiome to Molecular Interactions.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Sep 1;9(9):900. doi: 10.3390/jof9090900. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37755008 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metagenomics Applied to the Respiratory Mycobiome in Cystic Fibrosis.Mycopathologia. 2024 Sep 12;189(5):82. doi: 10.1007/s11046-024-00887-6. Mycopathologia. 2024. PMID: 39264513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical characteristics of people with cystic fibrosis and frequent fungal infection.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2022 Jan;57(1):152-161. doi: 10.1002/ppul.25741. Epub 2021 Nov 2. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2022. PMID: 34687280 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Microbiota and Mycobiota in Fungal Ball Rhinosinusitis: Specific Interaction between Aspergillus fumigatus and Haemophilus influenza?J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Jul 10;7(7):550. doi: 10.3390/jof7070550. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34356929 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Tigecycline Combined with Azithromycin Against Biofilms of Multidrug-Resistant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Isolates from a Patient in China.Infect Drug Resist. 2021 Feb 26;14:775-786. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S298274. eCollection 2021. Infect Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 33679134 Free PMC article.
-
Achromobacter xylosoxidans and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: Emerging Pathogens Well-Armed for Life in the Cystic Fibrosis Patients' Lung.Genes (Basel). 2021 Apr 21;12(5):610. doi: 10.3390/genes12050610. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33919046 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baldan R., Cigana C., Testa F., Bianconi I., De Simone M., Pellin D., et al. (2014). Adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis airways influences virulence of Staphylococcus aureus in vitro and murine models of co-infection. PLoS One 9:e89614. 10.1371/journal.pone.0089614 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

