Axon guidance pathway genes are associated with schizophrenia risk
- PMID: 30542400
- PMCID: PMC6257106
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6781
Axon guidance pathway genes are associated with schizophrenia risk
Abstract
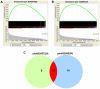
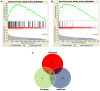
In the present study, we analyzed schizophrenia (SCZ)-related genome-wide association studies (GWAS) to identify genes and pathways associated with SCZ. We identified 1,098 common genes (1,098/9,468) and 20 shared KEGG pathways (both P<0.01) by integrating candidate genes from the European and American SCZ-related GWAS. The pathways related to axon guidance, long term potentiation and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) were highly significant (P<10-3). Moreover, 15 axon guidance pathway-related genes were associated with SCZ. The association between axon guidance pathway genes and SCZ was validated by a two-stage case-control study on Shandong migrants in northeastern China. Moreover, individuals with the rs9944880 TT polymorphism in the deleted in colorectal cancer (DCC) gene were associated with SCZ. These findings indicate that the axon guidance pathway genes and the rs9944880 SNP in DCC gene are associated with SCZ pathogenesis.
Keywords: Gene Set Enrichment Analysis; axon guidance; genome-wide association study; schizophrenia.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Integrating genome-wide association study and methylation functional annotation data identified candidate genes and pathways for schizophrenia.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2020 Jan 10;96:109736. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2019.109736. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 31425724
-
Identification of 34 genes conferring genetic and pharmacological risk for the comorbidity of schizophrenia and smoking behaviors.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Feb 3;12(3):2169-2225. doi: 10.18632/aging.102735. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32012119 Free PMC article.
-
Correlated expression analysis of genes implicated in schizophrenia: identification of putative disease-related pathways.New Horiz Transl Med. 2017 Jan;3(5):224-232. Epub 2016 Dec 10. New Horiz Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 32864408 Free PMC article.
-
How can genetics help understand the relationship between cognitive dysfunction and schizophrenia?Scand J Psychol. 2018 Feb;59(1):26-31. doi: 10.1111/sjop.12407. Scand J Psychol. 2018. PMID: 29356008 Review.
-
A large-scale integrative analysis of GWAS and common meQTLs across whole life course identifies genes, pathways and tissue/cell types for three major psychiatric disorders.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018 Dec;95:347-352. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.10.005. Epub 2018 Oct 16. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018. PMID: 30339835 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome Sequencing Reveals the Potential Mechanisms of Modified Electroconvulsive Therapy in Schizophrenia.Psychiatry Investig. 2021 May;18(5):385-391. doi: 10.30773/pi.2020.0410. Epub 2021 Apr 29. Psychiatry Investig. 2021. PMID: 33910328 Free PMC article.
-
Altered neuronal physiology, development, and function associated with a common chromosome 15 duplication involving CHRNA7.BMC Biol. 2021 Jul 28;19(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s12915-021-01080-7. BMC Biol. 2021. PMID: 34320968 Free PMC article.
-
UNC5C: Novel Gene Associated with Psychiatric Disorders Impacts Dysregulation of Axon Guidance Pathways.Genes (Basel). 2024 Feb 27;15(3):306. doi: 10.3390/genes15030306. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38540364 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying the differentially expressed peripheral blood microRNAs in psychiatric disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Psychiatry. 2024 May 17;15:1390366. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1390366. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38827444 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of the CO2 Extract of Eryngium planum L.Int J Biomater. 2023 Apr 27;2023:4702607. doi: 10.1155/2023/4702607. eCollection 2023. Int J Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37151378 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
