Effects of androgen and progestin on the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts
- PMID: 30542427
- PMCID: PMC6257455
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6772
Effects of androgen and progestin on the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts
Abstract
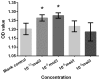
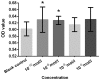
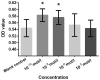
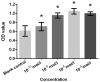
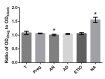
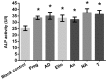
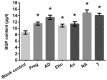
Osteoporosis is liable to affect patients with gonadal hormone deficiency, and a supplement of androgens may be used to increase bone density of patients with osteoporosis. Since the androgens currently used may cause severe side effects, it is useful to investigate the effect of other androgens and progestin on bone improvement. The aim of the current study was to investigate the effects of pregnenolone (Preg), androstenedione (AD), etiocholanolone (Etio), androsterone (An), nandrolone (NA) and testosterone (T) on the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts for potential clinical applications. Human osteoblasts were cultured and treated with androgens and progestin, including Preg, AD, Etio, An, NA, and T, at concentrations of 0, 10-10, 10-8, 10-6 and 10-5 mol/l. The levels of cell proliferation, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity and osteocalcin content were measured and assessed. Preg, AD, Etio, An, and T at concentrations of 10-10 and/or 10-8 mol/l significantly improved osteoblast proliferation. NA at concentrations of 10-10, 10-8, 10-6 and 10-5 mol/l also significantly improved osteoblast proliferation. Preg, AD, Etio, An, NA, and T significantly increased ALP activity and osteocalcin content. The present study demonstrated, for the first time, that Preg, AD, Etio, An, and NA could improve the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts in vitro.
Keywords: androgen; androstenedione; androsterone; etiocholanolone; nandrolone; osteoblasts; pregnenolone; testosterone.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of gonadal and adrenal androgens in a novel androgen-responsive human osteoblastic cell line.J Cell Biochem. 1998 Oct 1;71(1):96-108. J Cell Biochem. 1998. PMID: 9736458
-
[Dose-dependent effects of daidzein in regulating bone formation through estrogen receptors and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ].Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2011 Feb;9(2):165-72. doi: 10.3736/jcim20110209. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2011. PMID: 21288452 Chinese.
-
[Effects of progesterone on proliferation and differentiation of fetal rat calvarial osteoblasts in vitro].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 1997 Sep;32(9):538-40. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 1997. PMID: 9639754 Chinese.
-
Cellular and molecular effects of growth hormone and estrogen on human bone cells.APMIS Suppl. 1997;71:1-30. APMIS Suppl. 1997. PMID: 9357492 Review.
-
[Bone and Men's Health. The role of androgens in bone metabolism].Clin Calcium. 2010 Feb;20(2):165-73. Clin Calcium. 2010. PMID: 20118507 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Nandrolone induces a stem cell-like phenotype in human hepatocarcinoma-derived cell line inhibiting mitochondrial respiratory activity.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 10;10(1):2287. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58871-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32041983 Free PMC article.
-
Endocrinal metabolic regulation on the skeletal system in post-menopausal women.Front Physiol. 2022 Nov 11;13:1052429. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1052429. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36439254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in the pathogenesis of hepatic osteodystrophy and the potential therapeutic of mesenchymal stromal cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Dec 12;14(1):359. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03605-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 38087318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relation of testosterone level and other factors with bone mineral density in male kidney transplant recipients: a cross-sectional study.BMC Nephrol. 2023 Sep 14;24(1):271. doi: 10.1186/s12882-023-03318-8. BMC Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37710199 Free PMC article.
-
Osteogenic differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cell in the presence of testosterone and 17 β-estradiol in vitro.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2022 Feb;58(2):179-188. doi: 10.1007/s11626-022-00652-3. Epub 2022 Feb 17. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2022. PMID: 35175493
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
