Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR overexpression improves premature ovarian failure by upregulating Notch-1 expression
- PMID: 30542434
- PMCID: PMC6257585
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6750
Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR overexpression improves premature ovarian failure by upregulating Notch-1 expression
Abstract
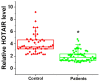
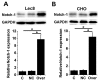
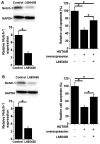
The aim of the present study was to investigate the role of long non-coding (lnc)RNA HOTAIR in premature ovarian failure. A total of 69 women with spontaneous premature ovarian failure and 48 healthy women were enrolled in the present study. Ovarian tissues and blood samples were harvested from each participant. The expression of HOTAIR in ovarian tissues and sera was detected using reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction. A receiver operator characteristic curve analysis was performed to assess the diagnostic value of HOTAIR expression in ovarian tissues and sera for premature ovarian failure. Hamster ovary cell lines overexpressing HOTAIR were established and cell apoptosis were assessed using an MTT assay. The effect of HOTAIR upregulation on the expression of Notch-1 was measured using western blotting. The expression of HOTAIR in ovarian tissues and serum samples was significantly lower in patients with premature ovarian failure compared with healthy controls. These results suggest that ovarian and serum HOTAIR expression levels may be used to accurately predict the risk of premature ovarian failure. It was also demonstrated that HOTAIR overexpression upregulates Notch-1 protein expression in hamster ovary cells and reduced apoptosis, whereas the Notch inhibitor L685458 ameliorated these effects. In conclusion, the results of the present study suggest that LncRNA HOTAIR overexpression improves premature ovarian failure by upregulating the expression of Notch-1.
Keywords: Notch-1; apoptosis; diagnosis; long non-coding RNA HOTAIR; premature ovarian failure.
Figures


Similar articles
-
LncRNA HOTAIR improves diabetic cardiomyopathy by increasing viability of cardiomyocytes through activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Dec;16(6):4817-4823. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6755. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30542437 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes cancer cell energy metabolism in pancreatic adenocarcinoma by upregulating hexokinase-2.Oncol Lett. 2019 Sep;18(3):2212-2219. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10551. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31452722 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of long non-coding RNA nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 inhibits the expression of p53 and improves premature ovarian failure.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Nov;20(5):69. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9197. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32963599 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA DRHC inhibits the proliferation of cancer cells in triple negative breast cancer by downregulating long non-coding RNA HOTAIR.Oncol Lett. 2019 Oct;18(4):3817-3822. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10683. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31516593 Free PMC article.
-
The long noncoding RNA HOTAIR serves as a microRNA-34a-5p sponge to reduce nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis via a NOTCH1-mediated mechanism.Gene. 2019 Oct 5;715:144029. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.144029. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Gene. 2019. PMID: 31376409 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Expression of long noncoding RNAs in the ovarian granulosa cells of women with diminished ovarian reserve using high-throughput sequencing.J Ovarian Res. 2022 Oct 29;15(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s13048-022-01053-6. J Ovarian Res. 2022. PMID: 36309699 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR drives EZH2-dependent myofibroblast activation in systemic sclerosis through miRNA 34a-dependent activation of NOTCH.Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Apr;79(4):507-517. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216542. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020. PMID: 32041748 Free PMC article.
-
The functional role of lncRNAs as ceRNAs in both ovarian processes and associated diseases.Noncoding RNA Res. 2023 Nov 18;9(1):165-177. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2023.11.008. eCollection 2024 Mar. Noncoding RNA Res. 2023. PMID: 38075201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNA-mediated granulosa cell dysfunction during ovarian aging: From mechanisms to potential interventions.Noncoding RNA Res. 2025 Mar 3;12:102-115. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2025.03.001. eCollection 2025 Jun. Noncoding RNA Res. 2025. PMID: 40144342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
lncRNA-FMR6 directly binds SAV1 to increase apoptosis of granulosa cells in premature ovarian failure.J Ovarian Res. 2023 Apr 1;16(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s13048-023-01121-5. J Ovarian Res. 2023. PMID: 37005611 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
