The exogenous administration of CB2 specific agonist, GW405833, inhibits inflammation by reducing cytokine production and oxidative stress
- PMID: 30542446
- PMCID: PMC6257606
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6753
The exogenous administration of CB2 specific agonist, GW405833, inhibits inflammation by reducing cytokine production and oxidative stress
Abstract
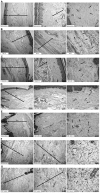
The present study aimed to investigate the role of cannabinoid 2 (CB2) receptors in a rat model of acute inflammation. Therefore, the potential of anti-inflammatory effects of CB2 receptor agonist (GW405833), CB2 receptor antagonist (AM630), and diclofenac, were investigated in carrageenan induced paw oedema in rats: as were assessed by measuring paw oedema; myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity in paw tissue; malondialdehyde (MDA) concentration; glutathione (GSH) level in paw tissue for oxidant/antioxidant balance; cytokine (interleukin-1β, IL-1β; tumour necrosis factor-α, TNF-α) levels in serum; histopathology of paw tissue for inflammatory cell accumulations. The results showed that GW405833 or diclofenac significantly reduced carrageenan-induced paw oedema. GW405833 also inhibited the increase of MPO activity, the recruitment of total leukocytes and neutrophils, and MDA concentration during carrageenan-induced acute inflammation, along with reversed nearly to the normal levels the increased of TNF-α, and IL-1β in serum. AM630 did not affect inflammation alone however clearly reversed the effects of agonist when co-administered. The mechanism of GW405833's suppression of inflammation is supported by these results, which are achieved by the inhibition of neutrophil migration, which regulates the reduction of oxidative stress, TNF-α and IL-1β levels. Finally, the activation of CB2 receptor, by selective agonist, has a major role in peripheral inflammation, and in the near future, targeting the peripheral cannabinoid system as a promising alternative to treat inflammation diseases may be considered a novel pharmacologic approach.
Keywords: CB2 receptor agonist; Carrageenan; GW405833; Paw oedema; oxidative stress.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phytol, a diterpene alcohol, inhibits the inflammatory response by reducing cytokine production and oxidative stress.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2014 Aug;28(4):455-64. doi: 10.1111/fcp.12049. Epub 2013 Sep 17. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24102680
-
Polysaccharide fraction isolated from Passiflora edulis inhibits the inflammatory response and the oxidative stress in mice.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2015 Jul;67(7):1017-27. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12399. Epub 2015 Mar 24. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25808583
-
Inhibition of inflammatory hyperalgesia by activation of peripheral CB2 cannabinoid receptors.Anesthesiology. 2003 Oct;99(4):955-60. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200310000-00031. Anesthesiology. 2003. PMID: 14508331
-
Pimaradienoic Acid Inhibits Carrageenan-Induced Inflammatory Leukocyte Recruitment and Edema in Mice: Inhibition of Oxidative Stress, Nitric Oxide and Cytokine Production.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 19;11(2):e0149656. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149656. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26895409 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation and peripheral 5-HT7 receptors: the role of 5-HT7 receptors in carrageenan induced inflammation in rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Sep 5;715(1-3):270-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.05.010. Epub 2013 Jun 3. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23742863
Cited by
-
Research progress on the cannabinoid type-2 receptor and Parkinson's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 Jan 8;15:1298166. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1298166. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38264546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Germ-free mice exhibit profound gut microbiota-dependent alterations of intestinal endocannabinoidome signaling.J Lipid Res. 2020 Jan;61(1):70-85. doi: 10.1194/jlr.RA119000424. Epub 2019 Nov 5. J Lipid Res. 2020. PMID: 31690638 Free PMC article.
-
β-Caryophyllene Inhibits Oxaliplatin-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice: Role of Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptors, Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Oct 22;12(10):1893. doi: 10.3390/antiox12101893. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37891972 Free PMC article.
-
The Expression of the Endocannabinoid Receptors CB2 and GPR55 Is Highly Increased during the Progression of Alzheimer's Disease in AppNL-G-F Knock-In Mice.Biology (Basel). 2023 May 31;12(6):805. doi: 10.3390/biology12060805. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372090 Free PMC article.
-
CB2 Agonist (AM1241) Improving Effect on Ovalbumin-Induced Asthma in Rats.Iran J Pharm Res. 2020 Winter;19(1):3-17. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2019.1101002. Iran J Pharm Res. 2020. PMID: 32922464 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
