The role of PI3-K/Akt signal pathway in the antagonist effect of CEPO on CHF rats
- PMID: 30542471
- PMCID: PMC6257438
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6822
The role of PI3-K/Akt signal pathway in the antagonist effect of CEPO on CHF rats
Abstract
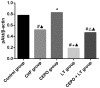
The possible role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3-K)/protein kinase B (Akt) signal pathway in the antagonist effect of carbamylated erythropoietin (CEPO) on chronic heart failure (CHF) in rats was investigated. Twenty of 120 rats were randomly selected as the control group, and the remaining rats as the model group. Rats in the model group received intraperitoneal injection of isoproterenol, those in the control group underwent intraperitoneal injection of equivalent normal saline. Rats with successful model establishment were divided into 4 groups, i.e. CHF group, CEPO group, LY294002 (LY) group and CEPO + LY group. Rats in the CEPO group underwent intraperitoneal injection of CEPO, while those in the CHF group received intraperitoneal injection of equivalent normal saline at the same time, those in the LY group received intraperitoneal injection of LY after model establishment, and those in the CEPO + LY group received the combined intraperitoneal injection of CEPO and LY simultaneously. Indicators for hemodynamics were determined using BL-410S bio-functional experiment system, including heart rate (HR), left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP), left ventricular systolic pressure (LVSP) and maximal increased rate of left ventricular pressure (LVP)/maximal reduced rate of LVP (±dp/dtmax). Western blotting assay was utilized to determine the changes in activity of PI3-K/Akt signal pathway. LVSP and ±dp/dtmax in the CHF, the CEPO, the CEPO + LY and the LY groups were significantly lower than those in the control group (P<0.05); LVSP and ±dp/dtmax in the CEPO group were also elevated significantly compared with CHF, LY and CEPO + LY groups (P<0.05) with significant decreases in LVEDP and HR (P<0.05); compared with the CHF group, LVSP and ±dp/dtmax in the LY group were each significantly decreased (P<0.05), in the LY group, pAkt level was significantly lower than that in the CHF group (P<0.05). In conclusion, CEPO can generate the antagonist effect on CHF in rats through activation of PI3-K/Akt signal pathway.
Keywords: CEPO; CHF; PI3-K/Akt; hemodynamics.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of Qiangxin Huoli decoction on rats with adriamycin-induced chronic heart failure.J Tradit Chin Med. 2019 Feb;39(1):81-88. J Tradit Chin Med. 2019. PMID: 32186027
-
Cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex control of cardiac function in normal and chronic heart failure states.J Physiol. 2017 Apr 15;595(8):2519-2534. doi: 10.1113/JP273764. Epub 2017 Feb 27. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28116751 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of total flavonoids of propolis on apoptosis of myocardial cells of chronic heart failure and its possible mechanism in rats].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2015 May;31(3):201-6. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26387177 Chinese.
-
[Moxibustion improves cardiac function by up-regulating autophagy-related proteins of cardiomyocytes in rats with chronic heart failure].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2019 Jan 25;44(1):25-30. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.170968. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2019. PMID: 30773858 Chinese.
-
Carbamylated Erythropoietin: A Prospective Drug Candidate for Neuroprotection.Biochem Insights. 2016 Feb 4;8(Suppl 1):25-9. doi: 10.4137/BCI.S30753. eCollection 2015. Biochem Insights. 2016. PMID: 26862298 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Network pharmacology combined with experimental analysis to explore the mechanism of the XinShuaiNing formula on heart failure.3 Biotech. 2025 May;15(5):110. doi: 10.1007/s13205-025-04288-4. Epub 2025 Apr 3. 3 Biotech. 2025. PMID: 40191450
References
-
- Ismailov RM. Global heart failure rates and erythropoietin. Iran J Med Hypotheses Ideas. 2012;6:70–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jmhi.2012.08.002. - DOI
-
- Zhang XJ, Liu J, Wan L, Sun Y, Wang F, Qi YJ, Huang CB. Relations of synovial angiogenesis and PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2015;28:71–74. (In Chinese) - PubMed
-
- Polat N, Oz F, Baykız D, Cizgici AY, Altun I, Buğra Z, Umman B, Tufan F, Oflaz H. Predictors of functional capacity in younger and elderly chronic heart failure patients: An observational study. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg. 2013;13:778–783. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
