Role of serum vitamin A and E in pregnancy
- PMID: 30542475
- PMCID: PMC6257734
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6830
Role of serum vitamin A and E in pregnancy
Abstract
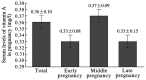
Serum levels of vitamin A and E in early, middle and late pregnancy were analyzed to evaluate vitamin nutritional status in pregnancy, and provide guidance for pregnant women about vitamin supplements in pregnancy. In total, 28,023 serum samples were randomly selected from pregnant women in early, middle and late pregnancy between January 2013 and June 2014 in Beijing. High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method was used to determine the concentration of serum vitamin A and E in pregnancy. The concentration of serum vitamin A in early, middle and late pregnancy was 0.33±0.08, 0.37±0.09 and 0.33±0.15 mg/l, respectively, total abnormal rate was 25.31%, and deficiency (24.98%) was the main feature. The rate of deficiency in the early pregnancy (38.22%) was greater than that in late pregnancy (35.13%). The serum vitamin E in early, middle and late pregnancy was 9.10±2.47, 14.24±3.66 and 15.80±5.01 mg/l, respectively, total abnormal rate was 5.60%, and excess (5.37%) was the main feature. The excess rate in early pregnancy was at the lowest level (0.50%), and reached the highest level (15.32%) in late pregnancy. The serum levels of vitamin A and E are different during pregnancy. Generally, vitamin A is deficient and vitamin E is in excess. Therefore, monitoring the vitamin A and E levels, and strengthening perinatal education and providing guidance for pregnant women to supply vitamins rationally play important role in guaranteeing maternal and fetal safety.
Keywords: nutritional status; pregnancy; serum levels; vitamin A; vitamin E.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Trend of vitamin A and vitamin E among pregnancy of Beijing in 2013-2016].Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2019 Jan;48(1):56-60. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2019. PMID: 31032768 Chinese.
-
[Study on anemia and vitamin A and vitamin D nutritional status of Chinese urban pregnant women in 2010-2012].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017 Feb 6;51(2):125-131. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2017.02.006. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28219150 Chinese.
-
[Serum vitamin A and E levels in pregnant women in Huai'an region from 2017 to 2018].Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2020 Jan;49(1):41-43. doi: 10.19813/j.cnki.weishengyanjiu.2020.01.007. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2020. PMID: 32290912 Chinese.
-
Influence of mineral and vitamin supplements on pregnancy outcome.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2012 Oct;164(2):127-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2012.06.020. Epub 2012 Jul 6. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2012. PMID: 22771225 Review.
-
The importance of beta-carotene as a source of vitamin A with special regard to pregnant and breastfeeding women.Eur J Nutr. 2007 Jul;46 Suppl 1:I1-20. doi: 10.1007/s00394-007-1001-z. Eur J Nutr. 2007. PMID: 17665093 Review.
Cited by
-
Determinants of the Essential Elements and Vitamins Intake and Status during Pregnancy: A Descriptive Study in Polish Mother and Child Cohort.Nutrients. 2021 Mar 16;13(3):949. doi: 10.3390/nu13030949. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33809457 Free PMC article.
-
Retinol and α-tocopherol in pregnancy: Establishment of reference intervals and associations with CBC.Matern Child Nutr. 2020 Jul;16(3):e12975. doi: 10.1111/mcn.12975. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Matern Child Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32141189 Free PMC article.
-
Review of evidence for environmental causes of uveal coloboma.Surv Ophthalmol. 2022 Jul-Aug;67(4):1031-1047. doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2021.12.008. Epub 2021 Dec 31. Surv Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 34979194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Antioxidant Applications for Combating 131I Side Effects in Thyroid Cancer Treatment.Toxics. 2023 Jun 13;11(6):529. doi: 10.3390/toxics11060529. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 37368629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Role of Mediterranean and Westernized Diets and Their Main Nutrients in the Modulation of Oxidative Stress in the Placenta: A Narrative Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Oct 26;12(11):1918. doi: 10.3390/antiox12111918. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38001771 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Buckley GJ, Murray-Kolb LE, Khatry SK, Leclerq SC, Wu L, West KJ, Jr, Christian P. Cognitive and motor skills in school-aged children following maternal vitamin A supplementation during pregnancy in rural Nepal: A follow-up of a placebo-controlled, randomised cohort. BMJ Open. 2013;3:e002000. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2012-002000. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Roberts JM, Myatt L, Spong CY, Thom EA, Hauth JC, Leveno KJ, Pearson GD, Wapner RJ, Varner MW, Thorp JM, Jr, et al. Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Maternal-Fetal Medicine Units Network: Vitamins C and E to prevent complications of pregnancy-associated hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1282–1291. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0908056. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
