Carotid thickness and atherosclerotic plaque stability, serum inflammation, serum MMP-2 and MMP-9 were associated with acute cerebral infarction
- PMID: 30542482
- PMCID: PMC6257476
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6868
Carotid thickness and atherosclerotic plaque stability, serum inflammation, serum MMP-2 and MMP-9 were associated with acute cerebral infarction
Abstract
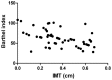
Correlations of carotid intima-media thickness (IMT), atherosclerotic plaque stability, serum inflammatory factors and serum matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 levels with the condition of disease in patients with acute cerebral infarction were analyzed to explore the predictive value of these risk factors. A total of 56 patients diagnosed with acute cerebral infarction in Jingmen First People's Hospital from February 2016 to January 2017 were selected and divided into the plaque stability group (n=25) and plaque instability group (n=31). Our results showed that the level of total cholesterol (TC) in the plaque instability group was significantly higher than that in the plaque stability group (P<0.05). IMT and National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score in the plaque instability group were significantly higher than those in the plaque stability group, but eccentricity index (EI) and Barthel index were significantly lower than those in the plaque stability group (P<0.05). The serum C-reactive protein (CRP), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels in the plaque instability group were significantly higher than those in the plaque stability group (P<0.05). The levels of serum MMP-2 and MMP-9 in the plaque instability group were significantly higher than those in the plaque stability group (P<0.05). Barthel index was correlated with IMT (r=-0.693, P<0.01), MMP-2 (r=-0.605, P<0.01), CRP (r=-0.765, P<0.01) and EI (r=0.811, P<0.01), respectively. Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), TC, systolic blood pressure, coronary heart disease, diabetes mellitus, IMT, EI, CRP, TNF-α, IL-6, MMP-2 and MMP-9 had independent predictive values for acute cerebral infarction (P<0.05). Carotid IMT, stability of the atherosclerotic plaque, serum inflammation, serum MMP-2 and MMP-9 levels have close correlations with acute cerebral infarction. The larger the carotid IMT is, the more unstable the plaque is and the higher the levels of serum inflammatory factors, MMP-2 and MMP-9 are, the greater the risk of acute cerebral infarction will be.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; carotid intima-media thickness; inflammatory factors; matrix metalloproteinase-9.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cluster of Differentiation 147 (CD147) serves as a promoter of atherosclerosis in patients with cerebral infarction.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022 Aug;26(16):5710-5717. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202208_29506. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36066144
-
Associations of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 concentrations with carotid atherosclerosis, based on measurements of plaque and intima-media thickness.Atherosclerosis. 2014 Jan;232(1):199-203. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.11.040. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Atherosclerosis. 2014. PMID: 24401238
-
Atherosclerosis is associated with plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 in chronic haemodialysis patients.Nephrology (Carlton). 2008 Oct;13(7):579-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1797.2008.00987.x. Nephrology (Carlton). 2008. PMID: 19161364
-
[The relationship between chronic periodontitis and the instability of carotid atherosclerotic plaque by serum level of MMP-9, MCP-1 and MMP-7].Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2015 Oct;24(5):589-93. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2015. PMID: 26598194 Chinese.
-
Hepatocyte growth factor, a biomarker of macroangiopathy in diabetes mellitus.World J Diabetes. 2014 Oct 15;5(5):678-88. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i5.678. World J Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 25317245 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of hub genes and regulatory networks in histologically unstable carotid atherosclerotic plaque by bioinformatics analysis.BMC Med Genomics. 2022 Jun 30;15(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s12920-022-01257-1. BMC Med Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35773742 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Neuroprotection of Artesunate and Tetramethylpyrazine in Ischemic Stroke, Mechanisms of Blood-Brain Barrier Preservation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 18;26(16):7979. doi: 10.3390/ijms26167979. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40869300 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Predictive Value of Tryptase, Serum Amyloid A and Lipoprotein-Associated Phospholipase A2 Biomarker Groups for Large Atherosclerotic Cerebral Infarction.Emerg Med Int. 2022 Oct 3;2022:5784909. doi: 10.1155/2022/5784909. eCollection 2022. Emerg Med Int. 2022. Retraction in: Emerg Med Int. 2023 Nov 29;2023:9798523. doi: 10.1155/2023/9798523. PMID: 36225714 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Feprazone Prevents Free Fatty Acid (FFA)-Induced Endothelial Inflammation by Mitigating the Activation of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway.ACS Omega. 2021 Feb 9;6(7):4850-4856. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c05826. eCollection 2021 Feb 23. ACS Omega. 2021. Retraction in: ACS Omega. 2024 Nov 15;9(47):47372. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c00977. PMID: 33644593 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Effect of intravenous thrombolysis with alteplase on clinical efficacy, inflammatory factors, and neurological function in patients with acute cerebral infarction.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2021 Mar 15;54(5):e10000. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X202010000. eCollection 2021. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2021. PMID: 33729386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ma LL, Song L, Yu XD, Yu TX, Liang H, Qiu JX. The clinical study on the treatment for acute cerebral infarction by intra-arterial thrombolysis combined with mild hypothermia. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21:1999–2006. - PubMed
-
- Segers D, Helderman F, Cheng C, van Damme LC, Tempel D, Boersma E, Serruys PW, de Crom R, van der Steen AF, Holvoet P, et al. Gelatinolytic activity in atherosclerotic plaques is highly localized and is associated with both macrophages and smooth muscle cells in vivo. Circulation. 2007;115:609–616. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.636415. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
