Novel fluid-fluid interface domains in geologic media
- PMID: 30542687
- PMCID: PMC7039256
- DOI: 10.1039/c8em00343b
Novel fluid-fluid interface domains in geologic media
Abstract
Pore-scale fluid processes in geological media are critical for numerous applications in several fields. Continued improvement of high-resolution image acquisition and processing methods has provided a means to directly characterize pore-scale fluid processes for natural geomedia, and to test the representativeness of theoretical and computational models developed to simulate them. High-resolution synchrotron X-ray microtomography (XMT) combined with advanced 3-D image visualization was used to investigate the impact of larger-scale solid-surface heterogeneity on nonwetting-wetting (air-water) interfacial area for two natural geomedia (a sand and a soil). The studies revealed the presence of air-water interfaces associated with water residing within macroscopic features such as pits and crevices on the surfaces of the solids. The diameters of the features ranged from tens to 100's of μm for the sand, and the aggregate associated air-water interfacial area was estimated to represent ∼12% of the maximum capillary interfacial area. These features and respective fluid interfaces, which are not considered in standard conceptualizations of fluid distribution in geomedia, may have an impact on pore-scale physical and biogeochemical processes.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


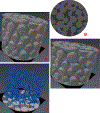



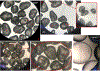

Similar articles
-
On the challenges of measuring interfacial characteristics of three-phase fluid flow with x-ray microtomography.J Microsc. 2014 Mar;253(3):171-82. doi: 10.1111/jmi.12106. Epub 2014 Jan 19. J Microsc. 2014. PMID: 24517255
-
Measuring air-water interfacial areas with X-ray microtomography and interfacial partitioning tracer tests.Environ Sci Technol. 2007 Mar 15;41(6):1956-61. doi: 10.1021/es061474m. Environ Sci Technol. 2007. PMID: 17410790
-
Influence of wettability and saturation on liquid-liquid interfacial area in porous media.Environ Sci Technol. 2003 Feb 1;37(3):584-91. doi: 10.1021/es020550s. Environ Sci Technol. 2003. PMID: 12630476
-
Recent Development of Durable and Self-Healing Surfaces with Special Wettability.Macromol Rapid Commun. 2016 Mar;37(6):463-85. doi: 10.1002/marc.201500591. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2016. PMID: 26833559 Review.
-
Multi-scale Cryptosporidium/sand interactions in water treatment.Water Res. 2006 Oct;40(18):3315-31. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2006.07.036. Epub 2006 Sep 18. Water Res. 2006. PMID: 16979211 Review.
Cited by
-
Pore-Scale Modeling of Fluid-Fluid Interfacial Area in Variably Saturated Porous Media Containing Microscale Surface Roughness.Water Resour Res. 2020 Jan;56(1):e2019WR025876. doi: 10.1029/2019wr025876. Epub 2019 Dec 26. Water Resour Res. 2020. PMID: 33408424 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the Micro-scale Surface Roughness Effect on Immiscible Fluids and Interfacial Areas in Porous Media Using the Measurements of Interfacial Partitioning Tracer Tests.Adv Water Resour. 2020 Dec;146:103789. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2020.103789. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Adv Water Resour. 2020. PMID: 33311835 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing XMT-Measurement Variability of Air-Water Interfacial Areas in Natural Porous Media.Water Resour Res. 2020 Jan;20(1):e2019WR025470. doi: 10.1029/2019WR025470. Epub 2019 Nov 17. Water Resour Res. 2020. PMID: 33184520 Free PMC article.
-
Examining the robustness and concentration dependency of PFAS air-water and NAPL-water interfacial adsorption coefficients.Water Res. 2021 Feb 15;190:116778. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116778. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Water Res. 2021. PMID: 33387950 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Culligan KA, Wildenschild D, Christensen BSB, Gray WG, Rivers ML and Tompson AFB, Interfacial area measurements for unsaturated flow through a porous medium, Water Resources Research, 2004, 40.
-
- Al-Raoush RI and Willson CS, Extraction of physically realistic pore network properties from three-dimensional synchrotron X-ray microtomography images of unconsolidated porous media systems, Journal of Hydrology, 2005, 300, 44–64.
-
- Schnaar G and Brusseau ML, Pore-scale characterization of organic immiscible-liquid morphology in natural porous media using synchrotron X-ray microtomography, Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39, 8403–8410. - PubMed
-
- Brusseau ML, Peng S, Schnaar G and Costanza-Robinson MS, Relationships among air-water interfacial area, capillary pressure, and water saturation for a sandy porous medium, Water Resources Research, 2006, 42.
-
- Culligan KA, Wildenschild D, Christensen BSB, Gray WG and Rivers ML, Pore-scale characteristics of multiphase flow in porous media: A comparison of air–water and oil–water experiments, Advances in Water Resources, 2006, 29, 227–238.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

