Anoikis‑resistant human osteosarcoma cells display significant angiogenesis by activating the Src kinase‑mediated MAPK pathway
- PMID: 30542722
- PMCID: PMC6278590
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2018.6827
Anoikis‑resistant human osteosarcoma cells display significant angiogenesis by activating the Src kinase‑mediated MAPK pathway
Abstract
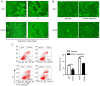
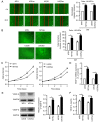
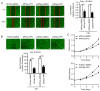
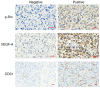
Tumor cells must resist anoikis to metastasize. There is a key role of angiogenesis in the growth and metastasis of tumors. However, the relationship between anoikis resistance and angiogenesis has not been well explored in human osteosarcoma. In the present study, we reported the higher expression of vascular endothelial growth factor‑A (VEGF‑A) in osteosarcoma cells that were resistant to anoikis than in parental osteosarcoma cells, promoting the proliferation, tube formation, and migration of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Src, JNK (Jun amino‑terminal kinase) and ERK (extracellular signal‑regulated kinase) signaling pathway phosphorylation was activated in anoikis‑resistant cells; Src inhibitor reduced the expression of VEGF‑A and angiogenesis and inhibited JNK and ERK pathway activity. Overexpression of phosphorylated (p)‑Src and VEGF‑A was positively correlated to the metastatic potential in human osteosarcoma tissues, as quantified by immunohistochemistry. In addition, p‑Src expression was directly correlated with VEGF‑A expression and microvessel density in vivo. Our findings revealed that anoikis resistance in osteosarcoma cells increased the expression of VEGF‑A and angiogenesis through the Src/JNK/ERK signaling pathways. Thus, Src may be a potential therapeutic alternative in osteosarcoma angiogenesis and metastasis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CCL3 promotes angiogenesis by dysregulation of miR-374b/ VEGF-A axis in human osteosarcoma cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 26;7(4):4310-25. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6708. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26713602 Free PMC article.
-
CCL5/CCR5 axis induces vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated tumor angiogenesis in human osteosarcoma microenvironment.Carcinogenesis. 2015 Jan;36(1):104-14. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgu218. Epub 2014 Oct 20. Carcinogenesis. 2015. PMID: 25330803
-
RanBP9/TSSC3 complex cooperates to suppress anoikis resistance and metastasis via inhibiting Src-mediated Akt signaling in osteosarcoma.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Dec 29;7(12):e2572. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.436. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 28032865 Free PMC article.
-
MCPIP1 promotes cell proliferation, migration and angiogenesis of glioma via VEGFA-mediated ERK pathway.Exp Cell Res. 2022 Sep 1;418(1):113267. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2022.113267. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Exp Cell Res. 2022. PMID: 35752346 Review.
-
Understanding micrometastatic disease and Anoikis resistance in ewing family of tumors and osteosarcoma.Oncologist. 2010;15(6):627-35. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2010-0093. Epub 2010 May 17. Oncologist. 2010. PMID: 20479280 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anoikis-related long non-coding RNA signatures to predict prognosis and small molecular drug response in cervical cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 20;14:1135626. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1135626. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37021052 Free PMC article.
-
Increased DEF6 expression is correlated with metastasis and poor prognosis in human osteosarcoma.Oncol Lett. 2020 Aug;20(2):1629-1640. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11743. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32724404 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of inhibition effect of daidzein on osteosarcoma cells based on experimental validation and systematic pharmacology analysis.PeerJ. 2021 Aug 31;9:e12072. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12072. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34540371 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic insights into the effects of Tris-2-butoxyethyl phosphate on multiple cancers using network toxicology and molecular docking.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 6;15(1):28781. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14733-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40770063 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of anoikis-related gene signatures and construction of the prognosis model in prostate cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 18;15:1383304. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1383304. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38957390 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

