Histone deacetylase SIRT6 regulates chemosensitivity in liver cancer cells via modulation of FOXO3 activity
- PMID: 30542728
- PMCID: PMC6196608
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2018.6770
Histone deacetylase SIRT6 regulates chemosensitivity in liver cancer cells via modulation of FOXO3 activity
Abstract
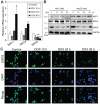
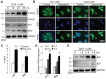
Liver cancer is the leading cause of cancer‑related mortality worldwide and its incidence is increasing. Considerable effort has been made in recent decades to improve the diagnosis and treatment of liver cancer. Advanced liver cancer often exhibits a poor response to chemotherapy and poor prognosis due to acquired chemoresistance and tumor recurrence. Understanding the precise molecular mechanisms that are responsible for chemotherapeutic drug‑induced cell death could potentially identify novel therapeutic targets and improve liver cancer treatment. In the present study, it was demonstrated that in response to doxorubicin, the most frequently used chemical compound for liver cancer treatment, histone deacetylase sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) is specifically downregulated. This enables forkhead box O3 (FOXO3) upregulation, translocation into the nucleus and increased expression of its target genes p27 and Bim, which further induce apoptosis. Overexpression of SIRT6, but not enzyme‑inactivated mutants, prevents FOXO3 translocation into the nucleus and doxorubicin‑induced cell death. SIRT6 interacts with FOXO3 and this interaction increases FOXO3 ubiquitination and decreases its stability. Finally, it was identified that the effect of SIRT6 in preventing doxorubicin‑induced cell death requires FOXO3. Overexpression of SIRT6 could not prevent doxorubicin‑induced cell death in FOXO3‑knockdown cells. Therefore, it was concluded that SIRT6 plays a central role in determining doxorubicin‑induced cell death via modulation of FOXO3 activity. Therapeutic targeting of SIRT6 and/or FOXO3 may offer novel strategies for treatment of liver cancer.
Figures



Similar articles
-
SIRT6 Overexpression Potentiates Apoptosis Evasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via BCL2-Associated X Protein-Dependent Apoptotic Pathway.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Jul 1;22(13):3372-82. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1638. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26861461
-
FOXO3-mediated chemo-protection in high-stage neuroblastoma depends on wild-type TP53 and SESN3.Oncogene. 2017 Nov 2;36(44):6190-6203. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.288. Epub 2017 Sep 4. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28869600 Free PMC article.
-
Forkhead box O3 promotes colon cancer proliferation and drug resistance by activating MDR1 expression.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019 Mar;7(3):e554. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.554. Epub 2019 Jan 8. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019. PMID: 30623608 Free PMC article.
-
The forkhead box O3 (FOXO3): a key player in the regulation of ischemia and reperfusion injury.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Mar 20;80(4):102. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04755-2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 36939886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Sirtuin 6 in the Deacetylation of Histone Proteins as a Factor in the Progression of Neoplastic Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 29;25(1):497. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010497. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203666 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Toxicity of Water-Soluble D-g-PNIPAM Polymers in a Complex with Chemotherapy Drugs and Mechanism of Their Action In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 6;25(5):3069. doi: 10.3390/ijms25053069. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474314 Free PMC article.
-
Sirt6 protects cardiomyocytes against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting P53/Fas-dependent cell death and augmenting endogenous antioxidant defense mechanisms.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023 Feb;39(1):237-258. doi: 10.1007/s10565-021-09649-2. Epub 2021 Oct 28. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 34713381
-
Sirtuin 6-A Key Regulator of Hepatic Lipid Metabolism and Liver Health.Cells. 2023 Feb 19;12(4):663. doi: 10.3390/cells12040663. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36831330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment Strategies and Metabolic Pathway Regulation in Urothelial Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 26;21(23):8993. doi: 10.3390/ijms21238993. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33256165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astragaloside IV, as a potential anticancer agent.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 17;14:1065505. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1065505. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36874003 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hadzic N, Finegold MJ. Liver neoplasia in children. Clin Liver Dis. 2011;15(443–462):vii–x. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

