Organic barn dust inhibits surfactant protein D production through protein kinase-c alpha dependent increase of GPR116
- PMID: 30543664
- PMCID: PMC6292596
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208597
Organic barn dust inhibits surfactant protein D production through protein kinase-c alpha dependent increase of GPR116
Abstract
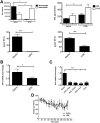
Prolonged exposure to organic barn dusts can lead to chronic inflammation and a broad range of lung problems over time, mediated by innate immune mechanisms. The immune surfactant or collectin surfactant protein D (SP-D) is a crucial multifunctional innate immune receptor. Little work to date has examined the effect of such collectins in response to organic dusts. We provide evidence here that agricultural organic dusts can inhibit mRNA and protein expression of SP-D in a human alveolar epithelial cell line, and an in vivo mouse model. This inhibition was not a result of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or peptidoglycans, the two most commonly cited immune active components of these dusts. We further show that inhibition of the signaling molecule protein kinase C alpha (PKCα) can reverse this inhibition implicating it as a mechanism of SP-D inhibition. Examination of the SP-D regulatory receptor GPR116 showed that its mRNA expression was increased in response to dust and inhibited by blocking PKCα, implicating it as a means of inhibiting SP-D in the lungs in response to organic dusts. This reduction shows that organic barn dust can reduce lung SP-D, thus leaving workers potentially at risk for a host of pathogens.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lung surfactant levels are regulated by Ig-Hepta/GPR116 by monitoring surfactant protein D.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 29;8(7):e69451. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069451. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23922714 Free PMC article.
-
Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia alters expression and distribution of lung collectins SP-A and SP-D.J Lab Clin Med. 2001 Jun;137(6):429-39. doi: 10.1067/mlc.2001.115220. J Lab Clin Med. 2001. PMID: 11385364
-
Effect of lung surfactant collectins on bronchoalveolar macrophage interaction with Blastomyces dermatitidis: inhibition of tumor necrosis factor alpha production by surfactant protein D.Infect Immun. 2006 Aug;74(8):4549-56. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00243-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16861641 Free PMC article.
-
Increased surfactant protein-D and foamy macrophages in smoking-induced mouse emphysema.Respirology. 2007 Mar;12(2):191-201. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2006.01009.x. Respirology. 2007. PMID: 17298450 Review.
-
Surfactant protein A and surfactant protein D variation in pulmonary disease.Immunobiology. 2007;212(4-5):381-416. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2007.01.003. Epub 2007 Feb 23. Immunobiology. 2007. PMID: 17544823 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of adhesion G protein-coupled receptor activation.J Biol Chem. 2020 Oct 9;295(41):14065-14083. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.007423. Epub 2020 Aug 6. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32763969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ozone Inhalation Attenuated the Effects of Budesonide on Aspergillus fumigatus-Induced Airway Inflammation and Hyperreactivity in Mice.Front Immunol. 2019 Sep 13;10:2173. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02173. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31572383 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical relevance of the adhesion G protein-coupled receptor F5 for human diseases and cancers.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2023 Jun;1869(5):166683. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.166683. Epub 2023 Mar 4. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2023. PMID: 36878303 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schiffman SS, Studwell CE, Landerman LR, Berman K, Sundy JS. Symptomatic effects of exposure to diluted air sampled from a swine confinement atmosphere on healthy human subjects. Environ Health Perspect. 2005;113: 567–576. 10.1289/ehp.6814 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vogelzang PFJ, Van Der Gulden JWJ, Folgering H, Heederik D, Tielen MJM, Van Schayck CP. Longitudinal changes in bronchial responsiveness associated with swine confinement dust exposure. Chest. 2000;117: 1488–1495. - PubMed
-
- Von Essen S, Romberger D. The Respiratory Inflammatory Response to the Swine Confinement Building Environment: The Adaptation to respiratory Exposures in the Chronically Exposed Worker. J Agric Saf Health. 2003;9: 185–196. - PubMed
-
- Poole JA, Romberger DJ. Immunological and inflammatory responses to organic dust in agriculture. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;12: 126–132. 10.1097/ACI.0b013e3283511d0e - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

