Guinea pig immunoglobulin VH and VL naïve repertoire analysis
- PMID: 30543679
- PMCID: PMC6292586
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208977
Guinea pig immunoglobulin VH and VL naïve repertoire analysis
Abstract
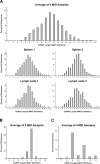
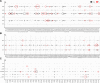
The guinea pig has been used as a model to study various human infectious diseases because of its similarity to humans regarding symptoms and immune response, but little is known about the humoral immune response. To better understand the mechanism underlying the generation of the antibody repertoire in guinea pigs, we performed deep sequencing of full-length immunoglobulin variable chains from naïve B and plasma cells. We gathered and analyzed nearly 16,000 full-length VH, Vκ and Vλ genes and analyzed V and J gene segment usage profiles and mutation statuses by annotating recently reported genome data of guinea pig immunoglobulin genes. We found that approximately 70% of heavy, 73% of kappa and 81% of lambda functional germline V gene segments are integrated into the actual V(D)J recombination events. We also found preferential use of a particular V gene segment and accumulated mutation in CDRs 1 and 2 in antigen-specific plasma cells. Our study represents the first attempt to characterize sequence diversity in the expressed guinea pig antibody repertoire and provides significant insight into antibody repertoire generation and Ig-based immunity of guinea pigs.
Conflict of interest statement
We have the following interests. Shun Matsuzawa is employed by Medical & Biological Laboratories Co., Ltd. There are no patents, products in development or marketed products to declare. This does not alter our adherence to all the PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials, as detailed online in the guide for authors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Variable region genes of anti-HIV human monoclonal antibodies: non-restricted use of the V gene repertoire and extensive somatic mutation.Mol Immunol. 1993 Nov;30(16):1543-51. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(93)90462-k. Mol Immunol. 1993. PMID: 8232339
-
Similarities and differences between the light and heavy chain Ig variable region gene repertoires in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Mol Med. 2006 Nov-Dec;12(11-12):300-8. doi: 10.2119/2006–00080.Ghiotto. Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 17380195 Free PMC article.
-
Somatic diversification and selection of immunoglobulin heavy and light chain variable region genes in IgG+ CD5+ chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells.J Exp Med. 1995 Apr 1;181(4):1507-17. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.4.1507. J Exp Med. 1995. PMID: 7535340 Free PMC article.
-
The repertoire of human antibody to the Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide.Int Rev Immunol. 1992;9(1):25-43. doi: 10.3109/08830189209061781. Int Rev Immunol. 1992. PMID: 1484268 Review.
-
[Immunoglobulin genes and the origin of antibody diversity].Rev Fr Transfus Hemobiol. 1992 Jan;35(1):47-65. doi: 10.1016/s1140-4639(05)80030-9. Rev Fr Transfus Hemobiol. 1992. PMID: 1590884 Review. French.
Cited by
-
The development of a highly sensitive and quantitative SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test applying newly developed monoclonal antibodies to an automated chemiluminescent flow-through membrane immunoassay device.BMC Immunol. 2023 Sep 26;24(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12865-023-00567-y. BMC Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37752417 Free PMC article.
-
Advantages and Limitations of Integrated Flagellin Adjuvants for HIV-Based Nanoparticle B-Cell Vaccines.Pharmaceutics. 2019 May 1;11(5):204. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11050204. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 31052410 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent antibody recognition profiles are generated by protective mRNA vaccines against Marburg and Ravn viruses.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):5702. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60057-0. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40595473 Free PMC article.
References
-
- de los Rios M, Criscitiello MF, Smider VV. Structural and genetic diversity in antibody repertoires from diverse species. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2015. August;33:27–41. 10.1016/j.sbi.2015.06.002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983. April;302(5909):575–81. - PubMed
-
- Teng G, Papavasiliou FN. Immunoglobulin Somatic Hypermutation. Annual Review of Genetics. 2007;41(1):107–20. - PubMed
-
- Jenne CN, Kennedy LJ, Reynolds JD. Antibody repertoire development in the sheep. Developmental & Comparative Immunology. 2006. January;30(1):165–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

