Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin (Siglec) 8 in patients with eosinophilic disorders: Receptor expression and targeting using chimeric antibodies
- PMID: 30543818
- PMCID: PMC6556424
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.10.066
Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin (Siglec) 8 in patients with eosinophilic disorders: Receptor expression and targeting using chimeric antibodies
Abstract
Background: Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin (Siglec) 8 is selectively expressed on eosinophils, mast cells, and basophils and, when engaged on eosinophils, can cause cell death.
Objective: We sought to characterize surface and soluble Siglec-8 (sSiglec-8) levels in normal donors (NDs) and eosinophilic donors (EOs) and assess the efficacy of anti-Siglec-8 antibodies in inducing eosinophil cell death in vitro.
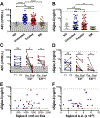
Methods: Eosinophil expression of Siglec-8 was assessed by using flow cytometry and quantitative PCR. Serum sSiglec-8 levels were measured by means of ELISA. Induction of eosinophil death by IgG4 (chimeric 2E2 IgG4) and afucosylated IgG1 (chimeric 2E2 IgG1 [c2E2 IgG1]) anti-Siglec-8 antibodies was evaluated in vitro by using flow cytometry and in vivo in humanized mice.
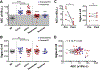
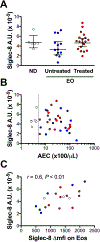
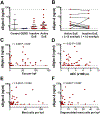
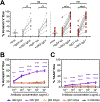
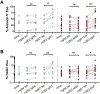
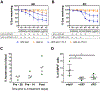
Results: Siglec-8 was consistently expressed on eosinophils from NDs and EOs and did not correlate with absolute eosinophil count or disease activity. sSiglec-8 levels were measurable in sera from most donors unrelated to absolute eosinophil counts or Siglec-8 surface expression. c2E2 IgG1 and chimeric 2E2 IgG4 were equally effective at inducing cell death (Annexin-V positivity) of purified eosinophils from NDs and EOs after overnight IL-5 priming. In contrast, killing of purified eosinophils without IL-5 was only seen in EOs, and natural killer cell-mediated eosinophil killing was seen only with c2E2 IgG1. Finally, treatment of humanized mice with anti-Siglec antibody led to robust depletion of IL-5-induced eosinophilia in vivo.
Conclusions: Siglec-8 is highly expressed on blood eosinophils from EOs and NDs and represents a potential therapeutic target for eosinophilic disorders. Enhanced killing of eosinophils in the presence of IL-5 might lead to increased efficacy in patients with IL-5-driven eosinophilia.
Keywords: Siglec-8; apoptosis; eosinophil; eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease; hypereosinophilic syndrome; inhibitory receptor; mast cell; mastocytosis; monoclonal antibody; soluble receptor.
Copyright © 2018 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
F.L., Y.C., J.W., X.Z., N.Z., S.R., J.M., K.R., M.M., I.M., D.D.M. and A.D.K. declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nutku E, Aizawa H, Hudson SA, Bochner BS. Ligation of Siglec-8: a selective mechanism for induction of human eosinophil apoptosis. Blood 2003;101:5014–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

