Positive N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Modulation by Rapastinel Promotes Rapid and Sustained Antidepressant-Like Effects
- PMID: 30544218
- PMCID: PMC6403082
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyy101
Positive N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Modulation by Rapastinel Promotes Rapid and Sustained Antidepressant-Like Effects
Abstract
Background: Modulation of glutamatergic synaptic transmission by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors can produce rapid and sustained antidepressant effects. Rapastinel (GLYX-13), initially described as a N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor partial glycine site agonist, exhibits rapid antidepressant effect in rodents without the accompanying dissociative effects of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists.
Methods: The relationship between rapastinel's in vitro N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor pharmacology and antidepressant efficacy was determined by brain microdialysis and subsequent pharmacological characterization of therapeutic rapastinel concentrations in N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-specific radioligand displacement, calcium mobilization, and medial prefrontal cortex electrophysiology assays.
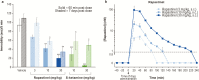
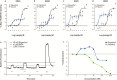
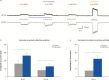
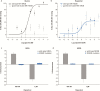
Results: Brain rapastinel concentrations of 30 to 100 nM were associated with its antidepressant-like efficacy and enhancement of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-dependent neuronal intracellular calcium mobilization. Modulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors by rapastinel was independent of D-serine concentrations, and glycine site antagonists did not block rapastinel's effect. In rat medial prefrontal cortex slices, 100 nM rapastinel increased N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated excitatory postsynaptic currents and enhanced the magnitude of long-term potentiation without any effect on miniature EPSCs or paired-pulse facilitation responses, indicating postsynaptic action of rapastinel. A critical amino acid within the NR2 subunit was identified as necessary for rapastinel's modulatory effect.
Conclusion: Rapastinel brain concentrations associated with antidepressant-like activity directly enhance medial prefrontal cortex N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activity and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated synaptic plasticity in vitro. At therapeutic concentrations, rapastinel directly enhances N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activity through a novel site independent of the glycine coagonist site. While both rapastinel and ketamine physically target N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors, the 2 molecules have opposing actions on N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Modest positive modulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors by rapastinel represents a novel pharmacological approach to promote well-tolerated, rapid, and sustained improvements in mood disorders.
Keywords: NMDA receptor; depression; rapastinel.
© The Author(s) 2018. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of CINP.
Figures


References
-
- Baron BM, Harrison BL, Kehne JH, Schmidt CJ, van Giersbergen PL, White HS, Siegel BW, Senyah Y, McCloskey TC, Fadayel GM, Taylor VL, Murawsky MK, Nyce P, Salituro FG (1997) Pharmacological characterization of MDL 105,519, an NMDA receptor glycine site antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol 323:181–192. - PubMed
-
- Berman RM, Cappiello A, Anand A, Oren DA, Heninger GR, Charney DS, Krystal JH (2000) Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry 47:351–354. - PubMed
-
- Burgdorf J, Kroes RA, Zhang XL, Gross AL, Schmidt M, Weiss C, Disterhoft JF, Burch RM, Stanton PK, Moskal JR (2015a) Rapastinel (GLYX-13) has therapeutic potential for the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder: characterization of a NMDA receptor-mediated metaplasticity process in the medial prefrontal cortex of rats. Behav Brain Res 294:177–185. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

