The Role of Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) in Regulating Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Thoracic Cancer
- PMID: 30544524
- PMCID: PMC6315659
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines6040114
The Role of Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) in Regulating Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Thoracic Cancer
Abstract
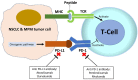
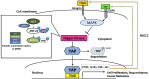
The programmed death-ligand 1(PD-L1)/PD-1 pathway is an immunological checkpoint in cancer cells. The binding of PD-L1 and PD-1 promotes T-cell tolerance and helps tumor cells escape from host immunity. Immunotherapy targeting the PD-L1/PD-1 axis has been developed as an anti-cancer therapy and used in treating advanced human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM). Yes-associated protein (YAP) is a key mediator of the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway, and plays important roles in promoting cancer development, drug resistance and metastasis in human NSCLC and MPM. YAP has been suggested as a new therapeutic target in NSCLC and MPM. The role of YAP in regulating tumor immunity such as PD-L1 expression has just begun to be explored, and the correlation between YAP-induced tumorigenesis and host anti-tumor immune responses is not well known. Here, we review recent studies investigating the correlation between YAP and PD-L1 and demonstrating the mechanism by which YAP regulates PD-L1 expression in human NSCLC and MPM. Future work should focus on the interactions between Hippo/YAP signaling pathways and the immune checkpoint PD-L1/PD-1 pathway. The development of new synergistic drugs for immune checkpoint PD-L1/PD-1 blockade in NSCLC and MPM is warranted.
Keywords: immunotherapy; malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM); non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1); yes-associated protein (YAP).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Pathway, Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) and the Regulation of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 5;20(15):3821. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153821. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31387256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of yes-associated protein down-regulates PD-L1 (CD274) expression in human malignant pleural mesothelioma.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Jun;22(6):3139-3148. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13593. Epub 2018 Mar 24. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29575535 Free PMC article.
-
YAP regulates PD-L1 expression in human NSCLC cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 9;8(70):114576-114587. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23051. eCollection 2017 Dec 29. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29383103 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin Downregulates PD-L1 Expression and Modulates Tumor Immunity in KRAS-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 26;22(11):5649. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115649. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34073318 Free PMC article.
-
PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade Therapy in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Current Status and Future Directions.Oncologist. 2019 Feb;24(Suppl 1):S31-S41. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-IO-S1-s05. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 30819829 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pan-cancer analysis of the prognostic and immunological role of hippo-YAP signaling pathway.Discov Oncol. 2024 Sep 27;15(1):504. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01212-9. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39333438 Free PMC article.
-
HMGB1 as a Potential Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for Malignant Mesothelioma.Dis Markers. 2019 Feb 12;2019:4183157. doi: 10.1155/2019/4183157. eCollection 2019. Dis Markers. 2019. PMID: 30891101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple signaling pathways in the frontiers of lung cancer progression.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 10;16:1593793. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1593793. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40557151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The YAP/TAZ Signaling Pathway in the Tumor Microenvironment and Carcinogenesis: Current Knowledge and Therapeutic Promises.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 31;23(1):430. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010430. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Crosstalk between Src and Hippo/YAP Signaling Pathways in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).Cancers (Basel). 2020 May 26;12(6):1361. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061361. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32466572 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

