Botanical Formulation HX109 Ameliorates TP-Induced Benign Prostate Hyperplasia in Rat Model and Inhibits Androgen Receptor Signaling by Upregulating Ca2+/CaMKKβ and ATF3 in LNCaP Cells
- PMID: 30544543
- PMCID: PMC6316726
- DOI: 10.3390/nu10121946
Botanical Formulation HX109 Ameliorates TP-Induced Benign Prostate Hyperplasia in Rat Model and Inhibits Androgen Receptor Signaling by Upregulating Ca2+/CaMKKβ and ATF3 in LNCaP Cells
Abstract
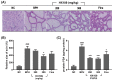
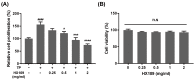
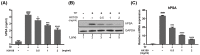
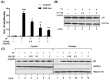
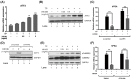
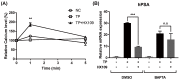
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a common disease in the elderly male population throughout the world. Among other factors, androgen dysregulation has been known to play major roles in its pathogenesis. HX109 is a botanical formulation prepared from a mixture of Taraxacum officinale, Cuscuta australis, and Nelumbo nucifera, which have traditionally been used-usually along with other plants-to treat urinary diseases. An ethanol extract was prepared from a mixture of these three plants, and its quality was controlled through cell-based bioassays and by quantification of several marker compounds by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). In the testosterone propionate (TP)-induced prostate hyperplasia rat model, oral administration of HX109 ameliorated prostate enlargement and histological changes induced by TP. In LNCaP cells, a human prostate epithelial cell line, HX109 repressed AR-mediated cell proliferation and the induction of androgen receptor (AR) target genes at the transcriptional level without affecting the translocation or expression of AR. Such effects of HX109 on AR signaling were mediated through the control of activating transcriptional factor 3 (ATF3) expression, phosphorylation of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase β (CaMKKβ), and increases in intracellular calcium, as evidenced by data from experiments involving ATF3-specific siRNA, CaMKKβ inhibitor, and calcium chelator, respectively. Taken together, our data suggest that HX109 might be used as a starting point for developing therapeutic agents for the treatment of BPH.
Keywords: AR signaling; ATF3; BPH; CaMKKβ; HX109.
Conflict of interest statement
W.L., D.S.L., I.-J.N., N.Y., Y.J., and S.K. are the employees of ViroMed Co. Ltd. S.K. owns stocks of this company. Other authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Botanical preparation HX109 inhibits macrophage-mediated activation of prostate epithelial cells through the CCL4-STAT3 pathway: implication for the mechanism underlying HX109 suppression of prostate hyperplasia.Heliyon. 2020 Jun 23;6(6):e04267. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04267. eCollection 2020 Jun. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32613128 Free PMC article.
-
Chrysophanic acid reduces testosterone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia in rats by suppressing 5α-reductase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 7;8(6):9500-9512. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13430. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27880726 Free PMC article.
-
Quisqualis indica Improves Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia by Regulating Prostate Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis.Biol Pharm Bull. 2017 Dec 1;40(12):2125-2133. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b17-00468. Epub 2017 Sep 22. Biol Pharm Bull. 2017. PMID: 28943529
-
Stromal androgen receptor roles in the development of normal prostate, benign prostate hyperplasia, and prostate cancer.Am J Pathol. 2015 Feb;185(2):293-301. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2014.10.012. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Am J Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25432062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory processes affecting androgen receptor expression, stability, and function: potential targets to treat hormone-refractory prostate cancer.J Cell Biochem. 2006 Aug 15;98(6):1408-23. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20927. J Cell Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16619263 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of larval extracts from identified Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis against benign prostatic hyperplasia induced by testosterone in rats.Food Sci Nutr. 2021 Aug 6;9(10):5361-5369. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2460. eCollection 2021 Oct. Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34646508 Free PMC article.
-
Botanical preparation HX109 inhibits macrophage-mediated activation of prostate epithelial cells through the CCL4-STAT3 pathway: implication for the mechanism underlying HX109 suppression of prostate hyperplasia.Heliyon. 2020 Jun 23;6(6):e04267. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04267. eCollection 2020 Jun. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32613128 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McVary K.T. BPH: Epidemiology and comorbidities. Am. J. Manag. Care. 2006;12:S122–S128. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

