Differing Contributions of Classical Risk Factors to Type 2 Diabetes in Multi-Ethnic Malaysian Populations
- PMID: 30544761
- PMCID: PMC6313591
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph15122813
Differing Contributions of Classical Risk Factors to Type 2 Diabetes in Multi-Ethnic Malaysian Populations
Abstract
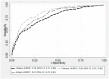
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes is escalating rapidly in Asian countries, with the rapid increase likely attributable to a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors. Recent research suggests that common genetic risk variants contribute minimally to the rapidly rising prevalence. Rather, recent changes in dietary patterns and physical activity may be more important. This nested case-control study assessed the association and predictive utility of type 2 diabetes lifestyle risk factors in participants from Malaysia, an understudied Asian population with comparatively high disease prevalence. The study sample comprised 4077 participants from The Malaysian Cohort project and included sub-samples from the three major ancestral groups: Malay (n = 1323), Chinese (n = 1344) and Indian (n = 1410). Association of lifestyle factors with type 2 diabetes was assessed within and across ancestral groups using logistic regression. Predictive utility was quantified and compared between groups using the Area Under the Receiver-Operating Characteristic Curve (AUC). In predictive models including age, gender, waist-to-hip ratio, physical activity, location, family history of diabetes and average sleep duration, the AUC ranged from 0.76 to 0.85 across groups and was significantly higher in Chinese than Malays or Indians, likely reflecting anthropometric differences. This study suggests that obesity, advancing age, a family history of diabetes and living in a rural area are important drivers of the escalating prevalence of type 2 diabetes in Malaysia.
Keywords: Asian populations; Malaysia; genetic; risk factor; rural; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation . IDF Diabetes Atlas. 8th ed. International Diabetes Federation; Brussels, Belgium: 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical