Identification of Two Novel Wheat Drought Tolerance-Related Proteins by Comparative Proteomic Analysis Combined with Virus-Induced Gene Silencing
- PMID: 30545152
- PMCID: PMC6321273
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19124020
Identification of Two Novel Wheat Drought Tolerance-Related Proteins by Comparative Proteomic Analysis Combined with Virus-Induced Gene Silencing
Abstract
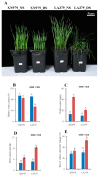
Drought is a major adversity that limits crop yields. Further exploration of wheat drought tolerance-related genes is critical for the genetic improvement of drought tolerance in this crop. Here, comparative proteomic analysis of two wheat varieties, XN979 and LA379, with contrasting drought tolerance was conducted to screen for drought tolerance-related proteins/genes. Virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) technology was used to verify the functions of candidate proteins. A total of 335 differentially abundant proteins (DAPs) were exclusively identified in the drought-tolerant variety XN979. Most DAPs were mainly involved in photosynthesis, carbon fixation, glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism, and several other pathways. Two DAPs (W5DYH0 and W5ERN8), dubbed TaDrSR1 and TaDrSR2, respectively, were selected for further functional analysis using VIGS. The relative electrolyte leakage rate and malonaldehyde content increased significantly, while the relative water content and proline content significantly decreased in the TaDrSR1- and TaDrSR2-knock-down plants compared to that in non-knocked-down plants under drought stress conditions. TaDrSR1- and TaDrSR2-knock-down plants exhibited more severe drooping and wilting phenotypes than non-knocked-down plants under drought stress conditions, suggesting that the former were more sensitive to drought stress. These results indicate that TaDrSR1 and TaDrSR2 potentially play vital roles in conferring drought tolerance in common wheat.
Keywords: Triticum aestivum L.; VIGS; comparative proteomic analysis; drought stress; iTRAQ.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Ingram J. A food systems approach to researching food security and its interactions with global environmental change. Food Secur. 2011;3:417–431. doi: 10.1007/s12571-011-0149-9. - DOI
-
- Rosegrant M.W., Ringler C., Zhu T. Water for agriculture: Maintaining food security under growing scarcity. Annu. Rev. Environ. Res. 2009;34:205–222. doi: 10.1146/annurev.environ.030308.090351. - DOI
-
- Thomas L. Why Wheat Matters. International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) [(accessed on 14 August 2014)];2014 Available online: http://www.cimmyt.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

