Structure of the posttranslational Sec protein-translocation channel complex from yeast
- PMID: 30545845
- PMCID: PMC6760253
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aav6740
Structure of the posttranslational Sec protein-translocation channel complex from yeast
Abstract
The Sec61 protein-conducting channel mediates transport of many proteins, such as secretory proteins, across the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane during or after translation. Posttranslational transport is enabled by two additional membrane proteins associated with the channel, Sec63 and Sec62, but its mechanism is poorly understood. We determined a structure of the Sec complex (Sec61-Sec63-Sec71-Sec72) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). The structure shows that Sec63 tightly associates with Sec61 through interactions in cytosolic, transmembrane, and ER-luminal domains, prying open Sec61's lateral gate and translocation pore and thus activating the channel for substrate engagement. Furthermore, Sec63 optimally positions binding sites for cytosolic and luminal chaperones in the complex to enable efficient polypeptide translocation. Our study provides mechanistic insights into eukaryotic posttranslational protein translocation.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures
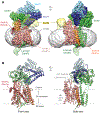

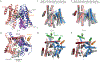
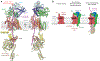
Comment in
-
Post-Translational Protein Transport by the Sec Complex.Trends Biochem Sci. 2019 Jun;44(6):481-483. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2019.03.003. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Trends Biochem Sci. 2019. PMID: 30962027
References
-
- Park E, Rapoport TA, Mechanisms of Sec61/SecY-mediated protein translocation across membranes. Annu Rev Biophys 41, 21–40 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Voorhees RM, Hegde RS, Toward a structural understanding of co-translational protein translocation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 41, 91–99 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Van den Berg B et al. , X-ray structure of a protein-conducting channel. Nature 427, 36–44 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

