Vagus-macrophage-hepatocyte link promotes post-injury liver regeneration and whole-body survival through hepatic FoxM1 activation
- PMID: 30546054
- PMCID: PMC6294142
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-07747-0
Vagus-macrophage-hepatocyte link promotes post-injury liver regeneration and whole-body survival through hepatic FoxM1 activation
Abstract
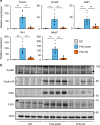
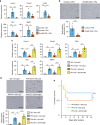
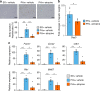
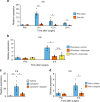
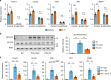
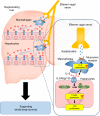
The liver possesses a high regenerative capacity. Liver regeneration is a compensatory response overcoming disturbances of whole-body homeostasis provoked by organ defects. Here we show that a vagus-macrophage-hepatocyte link regulates acute liver regeneration after liver injury and that this system is critical for promoting survival. Hepatic Foxm1 is rapidly upregulated after partial hepatectomy (PHx). Hepatic branch vagotomy (HV) suppresses this upregulation and hepatocyte proliferation, thereby increasing mortality. In addition, hepatic FoxM1 supplementation in vagotomized mice reverses the suppression of liver regeneration and blocks the increase in post-PHx mortality. Hepatic macrophage depletion suppresses both post-PHx Foxm1 upregulation and remnant liver regeneration, and increases mortality. Hepatic Il-6 rises rapidly after PHx and this is suppressed by HV, muscarinic blockade or resident macrophage depletion. Furthermore, IL-6 neutralization suppresses post-PHx Foxm1 upregulation and remnant liver regeneration. Collectively, vagal signal-mediated IL-6 production in hepatic macrophages upregulates hepatocyte FoxM1, leading to liver regeneration and assures survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Reticulon 4B (Nogo-B) facilitates hepatocyte proliferation and liver regeneration in mice.Hepatology. 2013 May;57(5):1992-2003. doi: 10.1002/hep.26235. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Hepatology. 2013. PMID: 23299899 Free PMC article.
-
Netrin-1 promotes liver regeneration possibly by facilitating vagal nerve repair after partial hepatectomy in mice.Cell Signal. 2022 Mar;91:110227. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.110227. Epub 2021 Dec 24. Cell Signal. 2022. PMID: 34954393
-
Defective Initiation of Liver Regeneration in Osteopontin-Deficient Mice after Partial Hepatectomy due to Insufficient Activation of IL-6/Stat3 Pathway.Int J Biol Sci. 2015 Aug 21;11(10):1236-47. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.12118. eCollection 2015. Int J Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26327817 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and biomarkers of liver regeneration after drug-induced liver injury.Adv Pharmacol. 2019;85:241-262. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2019.03.001. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Adv Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31307589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver Regeneration after Hepatectomy and Partial Liver Transplantation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 9;21(21):8414. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218414. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33182515 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tm7sf2 Disruption Alters Radial Gene Positioning in Mouse Liver Leading to Metabolic Defects and Diabetes Characteristics.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Nov 23;8:592573. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.592573. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33330474 Free PMC article.
-
Periportal hepatocyte proliferation at midgestation governs maternal glucose homeostasis in mice.Commun Biol. 2023 Dec 4;6(1):1226. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05614-3. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 38049528 Free PMC article.
-
β-adrenergic receptor agonist promotes ductular expansion during 3,5-diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-dihydrocollidine-induced chronic liver injury.Sci Rep. 2023 May 1;13(1):7084. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-33882-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37127664 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Features of Young and Aged Animals After Peripheral Nerve Injury: Implications for Diminished Regeneration Capacity.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Nov;43(8):4363-4375. doi: 10.1007/s10571-023-01431-8. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37922116 Free PMC article.
-
Liver Cancer Neuroscience: Regulating Liver Tumors via Selective Hepatic Vagotomy.Methods Protoc. 2024 Dec 11;7(6):99. doi: 10.3390/mps7060099. Methods Protoc. 2024. PMID: 39728619 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

