Novel insight into the function of tankyrase
- PMID: 30546421
- PMCID: PMC6256358
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.9551
Novel insight into the function of tankyrase
Abstract
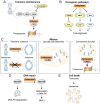
Tankyrases are multifunctional poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases that regulate a variety of cellular processes, including Wnt signaling, telomere maintenance and mitosis regulation. Tankyrases interact with target proteins and regulate their interactions and stability through poly(ADP-ribosyl) ation. In addition to their roles in telomere maintenance and regulation of mitosis, tankyrase proteins regulate tumor suppressors, including AXIN, phosphatase and tensin homolog and angiomotin. Therefore, tankyrases may be effective targets for cancer treatment. Tankyrase inhibitors could affect a variety of carcinogenic pathways that promote uncontrolled proliferation, including Wnt, AKT, yes-associated protein, telomere maintenance and mitosis regulation. Recently, novel aspects of the function and mechanism of tankyrases have been reported, and a number of tankyrase inhibitors have been identified. A combination of conventional chemotherapy agents with tankyrase inhibitors may have synergistic anticancer effects. Therefore, it is expected that more advanced and improved tankyrase inhibitors will be developed, enabling novel therapeutic strategies against cancer and other tankyrase-associated diseases. The present review discusses tankyrase function and the role of tankyrase inhibitors in the treatment of cancer.
Keywords: cancer therapy; novel tankyrase binding partners; post-translational modification; tankyrase; tankyrase inhibitors.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
