Lower trapezius transfer with semitendinosus tendon augmentation: Indication, technique, results
- PMID: 30546490
- PMCID: PMC6267376
- DOI: 10.1007/s11678-018-0495-8
Lower trapezius transfer with semitendinosus tendon augmentation: Indication, technique, results
Abstract
Background: Lower trapezius transfer can restore external rotation in brachial plexus palsies. In some cuff tear arthropathies, there is lack of active external rotation with a preservation of forward elevation. We evaluated the clinical outcomes of a lower trapezius transfer extended with a semitendinosus tendon and fixed to the insertion of the infraspinatus via arthroscopy.
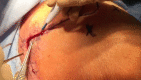
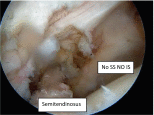
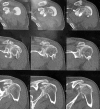
Methods: Between 2013 and 2016, we operated on 14 patients (8 men, 6 women; mean age of 62 years, range: 50-70) to reconstruct irreparable posterosuperior rotator cuff tear. A vertical incision of 6 cm following the medial border of the spine was made to harvest the lower trapezius in extension with the semitendinosus tendon. The extension band of the lower trapezius was fixed laterally via arthroscopy on the great tuberosity at the level of the insertion of the infraspinatus. The proximal stump of this extension band was then fixed medially into the muscle of the lower trapezius with the arm in maximum external rotation. Outcomes were evaluated with the Constant-Murley score, simple shoulder test (SST), and subjective shoulder value (SSV).
Results: Over a mean follow-up of 24 months (range: 12-36 months), the gain in external rotation with the arm at the side was 24° and 40° in 90° of abduction. The Constant-Murley score improved from 35 to 60 points, the SST from 3.5 to 7.5, the SSV from 30 to 60%, and the pain decreased from 7 to 2 (visual analogue scale, 0-10). Both the lag sign and hornblower sign were negative after this transfer. There were two cases of hematomas, and one was revised because of infection.
Conclusion: Lower trapezius transfer is a therapeutic option for irreparable posterosuperior cuff tears with a lack of active external rotation and a good subscapularis. Patients can expect improvements in pain and in active external rotation without any loss of active anterior elevation.
Hintergrund: Bei brachialen Plexuslähmungen kann ein Transfer des unteren Anteils des M. trapezius die Außenrotation wiederherstellen. Bei einigen manschettenrupturbedingten Arthropathien fehlt es an aktiver Außenrotation, während die Vorwärtshebung erhalten ist. Evaluiert wurden die klinischen Ergebnisse nach Transfer des mit einer Semitendinosus-Sehne verlängerten und arthroskopisch an den Ansatz des M. infraspinatus fixierten unteren Trapeziusanteils.
Methoden: Zwischen 2013 und 2016 wurden 14 Patienten (8 Männer, 6 Frauen; Durchschnittsalter 62 [50–70] Jahre) mit irreparabler posterosuperiorer Rotatorenmanschettenruptur rekonstruktiv operiert. Über einen 6 cm langen Schnitt am medialen Wirbelsäulenrand wurde der untere Anteil des M. trapezius in Verlängerung mit der Semitendinosussehne mobilisiert. Das „Verlängerungsband“ des unteren M. trapezius wurde arthroskopisch seitlich an der Tuberositas maior in Höhe des Ansatzes des M. infraspinatus fixiert. Der proximale Stumpf dieses Bandes wurde dann medial in den unteren Trapeziusanteil fixiert mit dem Arm in maximaler Außenrotation. Anhand des Constant-Murley-Scores, des SST („simple shoulder test“) und des SSV („subjective shoulder value“) wurde das Outcome evaluiert.
Ergebnisse: Nach einer durchschnittlichen Follow-up-Zeit von 24 (12–36) Monaten betrug der Funktionszuwachs hinsichtlich der Außenrotation bei an der Seite gehaltenem Arm in 90°-Abduktion 24° und 40°. Der Constant-Murley-Score hatte sich von 35 auf 60 Punkte verändert, der SST von 3,5 auf 7,5, der SSV von 30 auf 60 % und die Schmerzen von 7 auf 2 (visuelle Analogskala, 0–10). Nach dem Transfer waren sowohl das Lag- als auch das Hornblower-Zeichen negativ. Bei 2 Patienten kam es zu Hämatomen, bei einem zu einer infektionsbedingen Revision.
Fazit: Ein unterer Trapezius-Transfer ist eine therapeutische Option bei posterosuperiorer Rotatorenmanschettenruptur mit eingeschränkter aktiver Außenrotation und einer guten Subscapularis-Situation. Zu erwarten sind eine Schmerzlinderung und eine verbesserte aktive Außenrotation bei unveränderter aktiver Vorwärtshebung.
Keywords: Arthroscopy; Lack of active external rotation; Lower trapezius transfer; Rotator cuff tears; Shoulder.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical guidelinesP. Valenti and J.-D. Werthel receive royalties for shoulder prosthesis design from FH Orthopedics.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Arthroscopically Assisted Lower Trapezius Transfer Using Peroneus Longus Autograft for Irreparable Posterosuperior Rotator Cuff Tears.JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2025 Mar 18;15(1):e23.00047. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.ST.23.00047. eCollection 2025 Jan-Mar. JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2025. PMID: 40104526 Free PMC article.
-
[Latissimus dorsi transfer with a modified single-incision Herzberg technique and description of its arthroscopic advancement].Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2022 Feb;34(1):55-70. doi: 10.1007/s00064-021-00759-y. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2022. PMID: 35119483 German.
-
Recovery of active external rotation and elevation in young active men with irreparable posterosuperior rotator cuff tear using arthroscopically assisted latissimus dorsi transfer.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016 Sep;25(9):e265-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2015.12.011. Epub 2016 Mar 4. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016. PMID: 26952287
-
Lower trapezius transfer for massive posterosuperior rotator cuff defects.Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2022 Feb;34(1):34-44. doi: 10.1007/s00064-021-00756-1. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2022. PMID: 34918172 Review. English.
-
Pectoralis major and pectoralis minor transfer for irreparable subscapularis tendon tears.Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2022 Feb;34(1):45-54. doi: 10.1007/s00064-021-00760-5. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2022. PMID: 35113176 Review. English.
Cited by
-
Restoring the Anteroposterior Shoulder Force Couple: Arthroscopic-Assisted Lower Trapezius Tendon Transfer With Partially Augmented Rotator Cuff Repair for Irreparable Massive Rotator Cuff Tears.Arthrosc Tech. 2024 Aug 22;14(1):103176. doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2024.103176. eCollection 2025 Jan. Arthrosc Tech. 2024. PMID: 39989703 Free PMC article.
-
Arthroscopic-Assisted Lower Trapezius Transfer Augmented by Peroneus Longus Autograft in Irreparable Posterior Superior Rotator Cuff Tears: Functional Outcomes at 24 Months of Follow-up.Orthop J Sports Med. 2025 Apr 22;13(4):23259671251332602. doi: 10.1177/23259671251332602. eCollection 2025 Apr. Orthop J Sports Med. 2025. PMID: 40297054 Free PMC article.
-
Arthroscopic-assisted latissimus dorsi transfer for irreparable posterosuperior cuff tears: Clinical outcome of 15 patients.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2022 May;32(4):667-674. doi: 10.1007/s00590-021-03025-w. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2022. PMID: 34081197
-
Middle Trapezius Tendon Transfer for Augmentation of In Situ Superior Capsular Reconstruction-Reinforced Partial Rotator Cuff Repair: Short-term Outcomes of a Prospective Cohort Study.Orthop J Sports Med. 2023 Feb 17;11(2):23259671221147537. doi: 10.1177/23259671221147537. eCollection 2023 Feb. Orthop J Sports Med. 2023. PMID: 36814770 Free PMC article.
-
Arthroscopic Lower Trapezius Tendon Transfer for a Patient with Axillary Nerve Injury and Concomitant Rotator Cuff Tear: A Case Report and Technical Notes.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Oct 12;59(10):1817. doi: 10.3390/medicina59101817. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37893536 Free PMC article.
References
-
- RP Duncan, CM Jobin, M Chamberlain, S Numbari, Chi-Tsai-Tang, L M. Galatz. Lower trapezius tendon transfer for irreparable postero superior cuff tear. Wahsington University Orthopedics, BJHospital, Saint Louis Poster AAO 2014.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
