Intermittent Brugada syndrome in an anorexic adolescent girl
- PMID: 30546512
- PMCID: PMC6281732
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jccase.2014.03.012
Intermittent Brugada syndrome in an anorexic adolescent girl
Abstract
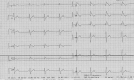
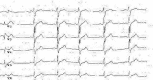
We report an anorexic adolescent girl with an intermittent Brugada syndrome. A 14-year-old anorexic girl with a body mass index (BMI) of 13.15 kg/m2 was admitted in the acute state of the disease with an ST elevation in V1 and V2, suggestive of Brugada syndrome. After 1 month of re-feeding, a control electrograph (ECG) was normal, but after an 8-month follow-up control with a nearly normal BMI, the ECG was again suggestive of Brugada syndrome. A genetic analysis of the gene SNC5A established a genetic change (p Leu 1582 pro), which provides the final explanation for the Brugada syndrome. Every rhythm problem in the acute state or during the re-feeding procedure deserves a strict follow-up to distinguish iatrogenic from heritable rhythm problems. <Learning objective: (i) We report the first case of a patient with anorexia nervosa with an intermittent Brugada syndrome. (ii) Moderate hypothermia can decrease the depolarization of pacemaker cells and cause ST-segment changes. (iii) Every rhythm problem in the acute state or during the re-feeding procedure deserves a strict follow-up to distinguish iatrogenic from heritable rhythm problems. (iv) A genetic analysis can make the distinction and is necessary to give advice for the future lifestyle of the patient.>.
Keywords: Anorexia nervosa; Brugada syndrome; Hypothermia; Iatrogenic; Weight loss.
Figures


References
-
- Bravender T., Kanter R., Zucker N. Anorexia nervosa and second-degree atrioventricular block (type I) Int J Eat Disord. 2006;39:612–615. - PubMed
-
- Bonnemeier H., Mäuser W., Schunkert H. Images in cardiovascular medicine. Brugada-like ECG pattern in severe hypothermia. Circulation. 2008;118:977–978. - PubMed
-
- Tamene A., Sattiraju S., Wang K., Benditt D.G. Brugada-like electrocardiography pattern induced by severe hyponatraemia. Europace. 2010;12:905–907. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

