Catheter ablation for Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome with coronary sinus diverticulum in a 15-year-old boy
- PMID: 30546634
- PMCID: PMC6280744
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jccase.2016.01.007
Catheter ablation for Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome with coronary sinus diverticulum in a 15-year-old boy
Abstract
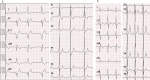
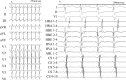
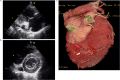
The left posterior and posteroseptal accessory pathways often have an epicardial accessory and are associated with coronary vein anomalies, such as diverticulum, fusiform, or bulbous enlargement. We report the case of a 15-year-old boy who suffered from palpitation due to Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome with coronary sinus diverticulum. An electrophysiology study revealed a left posterior accessory pathway and orthodromic atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia. After the transseptal puncture, we performed mapping around the mitral annulus during sinus rhythm. We could not detect typical atrioventricular fusion accompanied with accessory pathway potential and failed to ablate around the mitral annulus. We revealed typical accessory pathway potential in a coronary vein and successfully ablated. After ablation, a right atrium angiography showed a successful ablation site was just at the neck of coronary sinus diverticulum. It is important for a successful and safe ablation to evaluate coronary vein anomalies in patients with left posterior and posteroseptal accessory pathways. <Learning objective: In pediatric patients, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome with the posteroseptal accessory pathway with coronary sinus diverticulum is rare. It is important to predict the left posterior and posteroseptal accessory pathways from the polarity of the delta wave; ablation for pediatric patients seems to be more effective and safe in confirming coronary sinus diverticulum by echocardiogram before electrophysiology study and performing coronary vein angiography before mapping of the accessory pathway.>.
Keywords: Coronary sinus diverticulum; Radiofrequency catheter ablation; Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Successful catheter ablation of the accessory pathway in an unusual location in a 13-year-old girl with a coronary sinus diverticulum and Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.Cardiol Young. 2023 Nov;33(11):2375-2378. doi: 10.1017/S1047951123001117. Epub 2023 May 5. Cardiol Young. 2023. PMID: 37144400
-
Successful radiofrequency catheter ablation for wolff-Parkinson-white syndrome within the neck of a coronary sinus diverticulum.Korean Circ J. 2009 Sep;39(9):389-91. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2009.39.9.389. Epub 2009 Sep 30. Korean Circ J. 2009. PMID: 19949625 Free PMC article.
-
[Radiofrequency ablation of a posteroseptal accessory pathway associated with coronary sinus diverticulum].Rev Esp Cardiol. 1995 Sep;48(9):638-41. Rev Esp Cardiol. 1995. PMID: 7569268 Spanish.
-
Localization of left free-wall and posteroseptal accessory atrioventricular pathways by direct recording of accessory pathway activation.Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1989 Jan;12(1 Pt 2):204-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1989.tb02648.x. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1989. PMID: 2466254 Review.
-
Preprocedural Discrimination of Posteroseptal Accessory Pathways Ablated from the Right Endocardium from Those Requiring a Left-sided or Epicardial Coronary Venous Approach.Arrhythm Electrophysiol Rev. 2022 Apr;11:e07. doi: 10.15420/aer.2021.55. Arrhythm Electrophysiol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35734142 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High-risk accessory pathway associated with a rare right atrial diverticulum: a case report.Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2025 May 21;9(5):ytaf236. doi: 10.1093/ehjcr/ytaf236. eCollection 2025 May. Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40416881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arruda M.S., McClelland J.H., Wang X., Beckman K.J., Widman L.E., Gonzalez M.D., Nakagawa H., Lazzara R., Jackman W.M. Development and validation of an ECG algorithm for identifying accessory pathway ablation site in Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1998;9:2–12. - PubMed
-
- Jackman W.M., Wang X.Z., Friday K.J., Roman C.A., Moulton K.P., Beckman K.J., McClelland J.H., Twidale N., Hazlitt H.A., Prior M., Margolis P.D., Calame J.D., Overholt E.D., Lazzara R. Catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular pathways (Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome) by radiofrequency current. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:1605–1611. - PubMed
-
- Saad E.B., Marrouche N.F., Cole C.R., Natale A. Simultaneous epicardial and endocardial mapping of a left-sided posteroseptal accessory pathway associated with a large coronary sinus diverticulum: successful ablation by transection of the diverticulum's neck. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2002;25:1524–1526. - PubMed
-
- Sun Y., Arruda M., Otomo K., Beckman K., Nakagawa H., Calame J., Po S., Spector P., Lustgarten D., Herring L., Lazzara R., Jackman W. Coronary sinus-ventricular accessory connections producing posteroseptal and left posterior accessory pathways: incidence and electrophysiological identification. Circulation. 2002;106:1362–1367. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

