Exosomes impact survival to radiation exposure in cell line models of nervous system cancer
- PMID: 30546829
- PMCID: PMC6281426
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.26300
Exosomes impact survival to radiation exposure in cell line models of nervous system cancer
Abstract
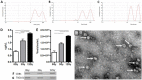
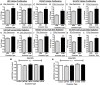
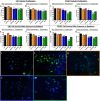
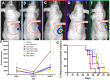
Radiation is utilized in the therapy of more than 50% of cancer patients. Unfortunately, many malignancies become resistant to radiation over time. We investigated the hypothesis that one method of a cancer cell's ability to survive radiation occurs through cellular communication via exosomes. Exosomes are cell-derived vesicles containing DNA, RNA, and protein. Three properties were analyzed: 1) exosome function, 2) exosome profile and 3) exosome uptake/blockade. To analyze exosome function, we show radiation-derived exosomes increased proliferation and enabled recipient cancer cells to survive radiation in vitro. Furthermore, radiation-derived exosomes increased tumor burden and decreased survival in an in vivo model. To address the mechanism underlying the alterations by exosomes in recipient cells, we obtained a profile of radiation-derived exosomes that showed expression changes favoring a resistant/proliferative profile. Radiation-derived exosomes contain elevated oncogenic miR-889, oncogenic mRNAs, and proteins of the proteasome pathway, Notch, Jak-STAT, and cell cycle pathways. Radiation-derived exosomes contain decreased levels of tumor-suppressive miR-516, miR-365, and multiple tumor-suppressive mRNAs. Ingenuity pathway analysis revealed the most represented networks included cell cycle, growth/survival. Upregulation of DNM2 correlated with increased exosome uptake. To analyze the property of exosome blockade, heparin and simvastatin were used to inhibit uptake of exosomes in recipient cells resulting in inhibited induction of proliferation and cellular survival. Because these agents have shown some success as cancer therapies, our data suggest their mechanism of action could be limiting exosome communication between cells. The results of our study identify a novel exosome-based mechanism that may underlie a cancer cell's ability to survive radiation.
Keywords: exosomes; glioblastoma; glioma; radiation; resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declares that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plasma exosome microRNAs are indicative of breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2016 Sep 8;18(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0753-x. Breast Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27608715 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of recipient cell-dependent differences in exosome uptake.BMC Cancer. 2018 Jan 6;18(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3958-1. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29306323 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome-mediated microRNA signaling from breast cancer cells is altered by the anti-angiogenesis agent docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).Mol Cancer. 2015 Jul 16;14:133. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0400-7. Mol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26178901 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome mediated communication within the tumor microenvironment.J Control Release. 2015 Dec 10;219:278-294. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.06.029. Epub 2015 Jul 2. J Control Release. 2015. PMID: 26143224 Review.
-
The multifaceted exosome: biogenesis, role in normal and aberrant cellular function, and frontiers for pharmacological and biomarker opportunities.Biochem Pharmacol. 2012 Jun 1;83(11):1484-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.12.037. Epub 2011 Dec 31. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22230477 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Radiation on Exosomes in Regulating Tumor Immune Microenvironment.Adv Radiat Oncol. 2024 Jul 4;9(8):101549. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2024.101549. eCollection 2024 Aug. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39055959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alerting the immune system to DNA damage: micronuclei as mediators.Essays Biochem. 2020 Oct 26;64(5):753-764. doi: 10.1042/EBC20200016. Essays Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32844183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of extracellular vesicles in acquisition of resistance to therapy in glioblastomas.Cancer Drug Resist. 2021 Mar 19;4(1):1-16. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2020.61. eCollection 2021. Cancer Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 35582008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trends in Research on Exosomes in Cancer Progression and Anticancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jan 17;13(2):326. doi: 10.3390/cancers13020326. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33477340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brownian Motion Influence on AFM Exosomes' Size Measurements.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 3;23(17):10074. doi: 10.3390/ijms231710074. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077470 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Allgeier A, Fisher B, Belanger K, Hau P, Brandes AA, Gijtenbeek J, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:459–66. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70025-7. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

