Focused ultrasound and Alzheimer's disease A systematic review
- PMID: 30546844
- PMCID: PMC6289486
- DOI: 10.1590/1980-57642018dn12-040003
Focused ultrasound and Alzheimer's disease A systematic review
Abstract
Alzheimer's disease (AD) affects millions of people, however, there is still no effective treatment. The use of focused ultrasound with microbubbles (FUS-MB) for the opening of the blood-brain barrier has been recently studied and may become a promising therapeutic target.
Objective: To discuss the use of FUS-MB for the treatment of AD and to present some of the techniques used.
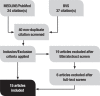
Methods: A systematic review was performed of MEDLINE/PubMed and Biblioteca Virtual em Saúde (BVS) services, using the keywords: focused ultrasound, Alzheimer, amyloid-b. Original articles were included in the study; studies that did not focus on Alzheimer's treatment were excluded.
Results: Fifteen original studies were selected. Preclinical trials were able to reduce amyloid-b plaques and tau phosphorylation, improving cognitive performance in AD animals.
Conclusion: The results are very promising, but the therapy still requires maturation. Further studies are needed to systematize all the techniques used and their effects in order to enable use in humans.
A doença de Alzheimer (DA) afeta milhões de pessoas, porém, ainda não há um tratamento efetivo. O uso de ultrassonografia focalizada com microbolhas (FUS-MB) para a abertura da barreira hematoencefálica (BHE) tem sido objeto de estudos recentes, podendo tornar-se um alvo terapêutico bastante promissor.
Objetivo: Discutir o uso da FUS-MB para o tratamento da DA e apresentar algumas das técnicas utilizadas.
Métodos: Revisão sistemática através dos serviços MEDLINE/PubMed e Biblioteca Virtual em Saúde (BVS), através das seguintes palavras-chaves: focused ultrasound, Alzheimer, amyloid-b. Foram incluídos no estudo artigos originais. Foram excluídos estudos que não tinham o tratamento do Alzheimer como foco.
Resultados: Foram selecionados 15 estudos originais. Os resultados pré-clínicos são positivos para redução de placas amiloides, fosforilação da proteína tau e sobre desempenho cognitivo de animais com DA.
Conclusão: Os resultados são promissores, mas terapia ainda necessita de aperfeiçoamento, necessitando de mais estudos que sistematize todas as técnicas e seus efeitos, para ser possível o seu uso em humanos.
Keywords: Alzheimer´s disease; amyloid-beta peptides; ultrasonic therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kumar A, Singh A. A review on Alzheimer's disease pathophysiology and its management: an update. Pharmacol Rep. 2015;67(2):195–203. - PubMed
-
- Bird TD. Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al. GeneReviews®. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1998. Oct 23, [2015 Sep 24]. Alzheimer Disease Overview. Internet. 1993-2018. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1161/
-
- Aprahamian I, Martinelli JE, Yassuda MS. Doença de Alzheimer: revisão da epidemiologia e diagnóstico. Rev Bras Clin Med. 2009;7(6):27–35.
-
- Meng Y, Volpini M, Black S, Lozano AM, Hynynen K, Lipsman N. Focused ultrasound as a novel strategy for Alzheimer disease therapeutics. Ann Neurol. 2017;81(5):611–617. - PubMed
-
- Kiessling F, Fokong S, Koczera P, Lederle W, Lammers T. Ultrasound microbubbles for molecular diagnosis, therapy, and theranostics. J Nucl Med. 2012;53(3):345–348. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous