Monitoring of drug treatment and psychosocial intervention with SPECT in Alzheimer patients Implications for neurologically appropriate psychosocial interventions. An observational study. The Osaki-Tajiri Project
- PMID: 30546848
- PMCID: PMC6289479
- DOI: 10.1590/1980-57642018dn12-040007
Monitoring of drug treatment and psychosocial intervention with SPECT in Alzheimer patients Implications for neurologically appropriate psychosocial interventions. An observational study. The Osaki-Tajiri Project
Abstract
We previously examined cerebral blood flow (CBF) with single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) in Alzheimer's disease (AD) with reference to drug treatment (donepezil) and psychosocial intervention.
Objective: The aim is to provide "brain-based" evidence for psychosocial interventions using SPECT.
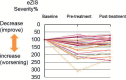
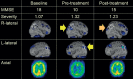
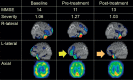
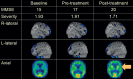
Methods: The participants were 27 consecutive outpatients with AD who received the drug and psychosocial intervention, and SPECT three times (baseline, pre-/post-intervention) at 6 month-intervals. The significance level of changes in CBF (Z score) and the extent of significantly changed areas, calculated with the eZIS system, were used as monitoring parameters. The participants were classified into three groups: improve (post-intervention CBF increased), worsening (progressive decline), and no change.
Results: Six, 8, and 13 patients were classified as improve, worsening, and no change, respectively. All subjects in the improve group showed improvement in cognitive test scores for the MMSE and/or the CGI scores associated with the brain area with a CBF increase (right parietal lobe), suggesting appropriate psychosocial intervention (visuospatial intervention).
Conclusion: These results suggest that monitoring of CBF with the eZIS system may be clinically applicable for monitoring of drug treatment and psychosocial intervention in AD patients.
Nós examinamos previamente o fluxo sanguíneo cerebral (FSC) com tomografia computadorizada de emissão de fóton único (SPECT) na doença de Alzheimer (DA) com referência ao tratamento medicamentoso (donepezila) e intervenção psicossocial.
Objetivo: Fornecer evidências “baseadas no cérebro” para intervenções psicossociais usando o SPECT.
Métodos: Os participantes foram 27 pacientes ambulatoriais consecutivos com DA que receberam a droga e intervenção psicossocial, e SPECT por três vezes (basal, pré/pós-intervenção) em intervalos de seis meses. O nível de significância das mudanças no FSC (escore Z) e a extensão das áreas significativamente alteradas calculadas com o sistema eZIS foram utilizados como parâmetros de monitoramento. Os participantes foram classificados em três grupos: melhora (FSC pós-intervenção aumentada), piora (declínio progressivo) e nenhuma mudança.
Resultados: Seis, oito e 13 pacientes foram classificados como melhora, piora e sem alteração, respectivamente. Todos no grupo melhora mostraram aumento dos escores no MEEM e/ou nos escores do CGI associados à área do cérebro com aumento do FSC (lobo parietal direito), sugerindo intervenção psicossocial apropriada (intervenção visoespacial).
Conclusão: Estes resultados sugerem que o monitoramento do FSC com o sistema eZIS pode ser clinicamente aplicável para o monitoramento do tratamento medicamentoso e intervenção psicossocial em pacientes com DA.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; SPECT; cerebral blood flow; donepezil; eZIS; monitoring; psychosocial intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors report no conflits of interst.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of a high dosage of donepezil for Alzheimer's disease as examined by single-photon emission computed tomography imaging.Psychogeriatrics. 2012 Sep;12(3):172-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-8301.2011.00399.x. Psychogeriatrics. 2012. PMID: 22994615
-
Improved Diagnostic Accuracy of SPECT Through Statistical Analysis and the Detection of Hot Spots at the Primary Sensorimotor Area for the Diagnosis of Alzheimer Disease in a Community-Based Study: "The Osaki-Tajiri Project".Clin Nucl Med. 2016 Jan;41(1):e1-6. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000000976. Clin Nucl Med. 2016. PMID: 26359573 Clinical Trial.
-
Utility of Easy Z-Score Imaging System-Assisted SPECT in Detecting Onset Age-Dependent Decreases in Cerebral Blood Flow in the Posterior Cingulate Cortex, Precuneus, and Parietal Lobe in Alzheimer's Disease with Amyloid Accumulation.Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra. 2020 Jun 10;10(2):63-68. doi: 10.1159/000507654. eCollection 2020 May-Aug. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra. 2020. PMID: 32774341 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral blood flow in patients with dementia of Alzheimer's type.Aging (Milano). 1993 Feb;5(1):19-26. doi: 10.1007/BF03324122. Aging (Milano). 1993. PMID: 8481422 Review.
-
Cerebral blood flow in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Ageing Res Rev. 2021 Nov;71:101450. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2021.101450. Epub 2021 Aug 19. Ageing Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 34419673
Cited by
-
Two-layer analytical model for estimation of layer thickness and flow using Diffuse Correlation Spectroscopy.PLoS One. 2022 Sep 16;17(9):e0274258. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274258. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36112634 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Butler RN. The life review: an interpretation of reminiscence in the aged. Psychiatry. 1963;26:65–76. - PubMed
-
- Taulbee LR, Holsom JC. Reality orientation for geriatric patients. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1966;17:133–135. - PubMed
-
- Baines S, Saxby P, Ehlert K. Reality orientation and reminiscence therapy: a control cross-over study of elderly confused people. Br J Psychiatry. 1987;1:222–231. - PubMed
-
- Goldwasser AN, Auerbach AM, Harkins SW. Cognitive, affective, and behavioral effects of reminiscence group therapy on demented elderly. Int J Aging Human Develop. 1987;25(3):209–222. - PubMed
-
- Tadaka E, Kanagawa K, Tachiura K, Wada M. Effects of care program of reminiscence on community elderly with dementia. Jap Acad Gerontol Nurs. 2000;5(1):96–106.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources