Association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D, hemoglobin A1c and fasting blood glucose levels in adults with diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 30546881
- PMCID: PMC6256128
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2018.1159
Association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D, hemoglobin A1c and fasting blood glucose levels in adults with diabetes mellitus
Abstract
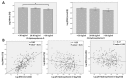
In the present study, the aim was to investigate the association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration and measures of glycemic control including hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) and fasting blood glucose (FBG) in adult patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) from the north of Jordan. Another aim was to compare serum levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D between patients with good glycemic control and patients with uncontrolled DM. This was a cross-sectional study that included 261 participants with DM. The concentration of 25-hydroxyvitamin D was measured using electrochemiluminescence immunoassay, HbA1c was measured using turbidimetric inhibition immunoassay and FBG was measured using the hexokinase method. Data regarding other clinical variables were obtained from medical records or by self-reporting. Participants with good glycemic control exhibited significantly higher levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D compared with participants with uncontrolled DM (P=0.03). Participants with sufficient vitamin D status (>30 ng/ml in serum) exhibited significantly lower HbA1c level compared with participants with deficient vitamin D (<20 ng/ml) status (P=0.02). Correlation analysis determined significant inverse correlations between 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and HbA1c and FBG levels (r=-0.23 and -0.17, respectively, both P<0.01). There were also significant correlations between duration of DM and HbA1c and FBG levels (both r=0.21, P<0.01). HbA1c level was also inversely correlated with participants' age (r=-0.19, P<0.01). Further multiple linear regression analysis revealed an inverse significant association between HbA1c and 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels (F=12.95, R2=0.48, P<0.01) but did not identify a similar association between FBG and 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels. These findings may encourage further research to identify if vitamin D supplementation may improve measures of glycemic control, and how vitamin D may affect glucose homeostasis in patients with DM.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; glycemic control; hemoglobin A1c; vitamin D.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Association Between Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and Glycemic Control in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus: A Single-Center Retrospective Study.J ASEAN Fed Endocr Soc. 2023;38(1):13-20. doi: 10.15605/jafes.038.01.04. Epub 2022 Dec 9. J ASEAN Fed Endocr Soc. 2023. PMID: 37252414 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of fasting glucose and glycated hemoglobin with vitamin D levels according to diabetes mellitus status in Korean adults.Epidemiol Health. 2022;44:e2022025. doi: 10.4178/epih.e2022025. Epub 2022 Feb 21. Epidemiol Health. 2022. PMID: 35209709 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of musculoskeletal pain in association with serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Biomed Rep. 2018 Jun;8(6):571-577. doi: 10.3892/br.2018.1093. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Biomed Rep. 2018. PMID: 29904613 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of vitamin D supplementation on indices of glycemic control in Iranian diabetics: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2019 Feb;34:294-304. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2018.12.009. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2019. PMID: 30712741
-
Significance of Educational Literature and Diabetes Log Sheet on Hemoglobin A1c.Cureus. 2022 Jan 27;14(1):e21667. doi: 10.7759/cureus.21667. eCollection 2022 Jan. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35233335 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Its Association in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Elderly Patients with Kidney Disease: A Retrospective Cross Sectional Study.Metabolites. 2023 Feb 28;13(3):357. doi: 10.3390/metabo13030357. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 36984797 Free PMC article.
-
25-Hydroxyvitamin D Is Associated with Islet Homeostasis in Type-2 Diabetic Patients with Abdominal Obesity.Curr Med Sci. 2023 Oct;43(5):919-926. doi: 10.1007/s11596-023-2780-z. Epub 2023 Sep 12. Curr Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37697161
-
Association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and fasting blood glucose in osteoporosis patients.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 1;13(1):18812. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45504-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37914715 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental Approaches to Diabetes Mellitus.Eurasian J Med. 2022 Dec;54(Suppl1):145-153. doi: 10.5152/eurasianjmed.2022.22304. Eurasian J Med. 2022. PMID: 36655459 Free PMC article.
-
The Association Between Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and Glycemic Control in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus: A Single-Center Retrospective Study.J ASEAN Fed Endocr Soc. 2023;38(1):13-20. doi: 10.15605/jafes.038.01.04. Epub 2022 Dec 9. J ASEAN Fed Endocr Soc. 2023. PMID: 37252414 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Qaseem A, Wilt TJ, Kansagara D, Horwitch C, Barry MJ, Forciea MA Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians, corp-author. Hemoglobin A1c targets for glycemic control with pharmacologic therapy for nonpregnant adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A guidance statement update from the American college of physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2018;168:569–576. doi: 10.7326/M17-0939. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
