Identification of PD-L2, B7-H3 and CTLA-4 immune checkpoint proteins in genetic subtypes of meningioma
- PMID: 30546952
- PMCID: PMC6287792
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2018.1512943
Identification of PD-L2, B7-H3 and CTLA-4 immune checkpoint proteins in genetic subtypes of meningioma
Abstract
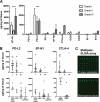
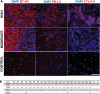
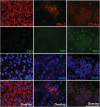
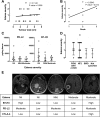
Meningioma is the most common brain tumor in adults. Surgical resection remains the primary treatment. No chemotherapy exists. However, gene mutations now could explain ~ 80% of meningioma and targeted therapies based on these are being investigated. Furthermore, with the recent discovery of PD-L1 in malignant meningioma, clinical trials using immunotherapy have commenced. Here, we report for the first time the expression profiles of immune checkpoint proteins PD-L2, B7-H3 and CTLA-4 in meningioma and their association to common gene mutations. PD-L2 and B7-H3 expression was significantly greater than all immune checkpoint proteins studied, and particularly elevated in patients with gene mutations affecting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. CTLA-4 expressing CD3+ lymphocytes were observed in atypical and malignant meningioma and tumors harboring a PIK3CA or SMO mutation. These results identify novel targets for immunotherapy irrespective of grade and distinguish potential patient populations based on genetic classification for stratification into checkpoint inhibitor clinical trials.
Keywords: B7-H3; CTLA-4; Meningioma; PD-L1; PD-L2; PI3K/AKT/mTOR; brain tumor; immune checkpoint protein; immunotherapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression and Clinical Significance of Immune Checkpoint Regulator B7-H3 (CD276) in Human Meningioma.World Neurosurg. 2020 Mar;135:e12-e18. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.10.044. Epub 2019 Oct 16. World Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 31629137
-
Immune Checkpoint Molecules on Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Their Association with Tertiary Lymphoid Structures in Human Breast Cancer.Front Immunol. 2017 Oct 30;8:1412. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01412. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29163490 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting PP2A Upregulates B7-H3 Expression and Potentially Increases the Sensitivity of Malignant Meningiomas to Immunotherapy by Proteomics.Pathol Oncol Res. 2022 Sep 20;28:1610572. doi: 10.3389/pore.2022.1610572. eCollection 2022. Pathol Oncol Res. 2022. PMID: 36203966 Free PMC article.
-
The Next Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors: PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade in Melanoma.Clin Ther. 2015 Apr 1;37(4):764-82. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.02.018. Epub 2015 Mar 29. Clin Ther. 2015. PMID: 25823918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B7 Family Members in Lymphoma: Promising Novel Targets for Tumor Immunotherapy?Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 31;11:647526. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.647526. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33869045 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Rapid Robust Method for Subgrouping Non-NF2 Meningiomas According to Genotype and Detection of Lower Levels of M2 Macrophages in AKT1 E17K Mutated Tumours.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 13;21(4):1273. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041273. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32070062 Free PMC article.
-
Drug target therapy and emerging clinical relevance of exosomes in meningeal tumors.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Jan;479(1):127-170. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04715-1. Epub 2023 Apr 4. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37016182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CTLA-4 expression on CD4+ lymphocytes in patients with sepsis-associated immunosuppression and its relationship to mTOR mediated autophagic-lysosomal disorder.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 22;15:1396157. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1396157. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39104530 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress of B7-H3 in malignant tumors.Front Immunol. 2025 May 30;16:1586759. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1586759. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40519928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic Characteristics of Invasive Mucinous Adenocarcinomas of the Lung and Potential Therapeutic Targets of B7-H3.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Nov 30;10(12):478. doi: 10.3390/cancers10120478. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30513627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Kleihues P, Ellison DW. The 2016 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131(6):803–820. doi:10.1007/s00401-016-1545-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
