Tumor-infiltrating neutrophils predict therapeutic benefit of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in metastatic renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 30546957
- PMCID: PMC6287784
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2018.1515611
Tumor-infiltrating neutrophils predict therapeutic benefit of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
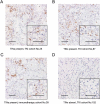
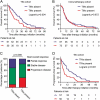
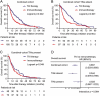
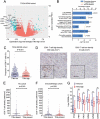
Tumor-infiltrating neutrophils (TINs) show diverse predictive effects in the context of different cancer types and therapeutic regimens. In this study we investigated their relevance with therapeutic effect of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). Two independent datasets including 271 mRCC patients treated by TKIs or IL-2/IFN-α based immunotherapy were retrospective included, and TINs were detected by immunohistochemistry. The presence of TINs was observed in 50 (45.0%) samples of the TKI cohort and in 73 (45.6%) samples of the immunotherapy cohort. TINs were associated with shorter overall survival (HR, 1.776; 95%CI, 1.191-2.650; p = 0.004) in the TKI cohort, but not in the immunotherapy cohort (HR, 1.074; 95%CI, 0.767-1.505; p = 0.672). Multivariate Cox analysis confirmed the independent prognostic value of TINs for TKI-treated patients (HR, 2.078, 95%CI, 1.352-3.195; p = 0.001), apart from other parameters. Moreover, survival benefit of TKI therapy was superior to IL-2/IFN-α immunotherapy only among TINs-absent patients (HR, 1.561; 95%CI, 0.927-2.629; p = 0.094). Data mining in the TCGA cohort of renal cell carcinoma revealed the predominant immunosuppressive function of TINs in renal cell carcinoma. The negative correlation between TINs and intratumoral CD8+ T cells was further confirmed in the TKI cohort (p = 0.019), the immunotherapy cohort (p = 0.001) and the TCGA cohort (p < 0.001). In conclusion, the presence of TINs was an independent, unfavorable prognostic factor in TKI-treated mRCC patients. TINs could also predict therapeutic benefit of TKIs over IL-2/IFN-α immunotherapy. These findings should be further confirmed within datasets of clinical trials or prospective observational studies.
Keywords: Metastatic renal cell carcinoma; immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment; survival; tumor-infiltrating neutrophils; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumor-Infiltrating Neutrophils Predict Poor Survival of Non-Functional Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Jul 1;105(7):dgaa196. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa196. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32285127
-
Spine stereotactic radiosurgery with concurrent tyrosine kinase inhibitors for metastatic renal cell carcinoma.J Neurosurg Spine. 2016 Dec;25(6):766-774. doi: 10.3171/2016.4.SPINE16229. Epub 2016 Jul 8. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016. PMID: 27391397
-
Tumor infiltrating CD19+ B lymphocytes predict prognostic and therapeutic benefits in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Oncoimmunology. 2018 Aug 6;7(10):e1477461. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2018.1477461. eCollection 2018. Oncoimmunology. 2018. PMID: 30288343 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-2 based immunotherapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.Dan Med Bull. 2007 Nov;54(4):249-65. Dan Med Bull. 2007. PMID: 18208677 Review.
-
Interleukin-6 induces drug resistance in renal cell carcinoma.Fukushima J Med Sci. 2018 Dec 8;64(3):103-110. doi: 10.5387/fms.2018-15. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Fukushima J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30369518 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Macrophage Phenotype in Combination with Tumor Microbiome Composition Predicts RCC Patients' Survival: A Pilot Study.Biomedicines. 2022 Jun 27;10(7):1516. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10071516. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35884821 Free PMC article.
-
Thymidine kinase 1 indicates resistance to immune checkpoint plus tyrosine kinase inhibition in renal cell carcinoma.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2025 Jun;48(3):775-787. doi: 10.1007/s13402-025-01048-7. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2025. PMID: 40009128 Free PMC article.
-
Intratumoral CXCL13+CD8+T cell infiltration determines poor clinical outcomes and immunoevasive contexture in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Feb;9(2):e001823. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001823. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33589528 Free PMC article.
-
Favorable Immunotherapy Plus Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition Outcome of Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients with Low CDK5 Expression.Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Oct;55(4):1321-1336. doi: 10.4143/crt.2022.1532. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Cancer Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 37024096 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Novel Glycolysis-Related Gene Signature Correlates With the Prognosis and Therapeutic Responses in Patients With Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 17;11:633950. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.633950. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33816274 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Oudard S, Negrier S, Szczylik C, Pili R, Bjarnason GA, et al. Overall survival and updated results for sunitinib compared with interferon alfa in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3584–3590. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.20.1293. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Tomczak P, Hutson TE, Michaelson MD, Negrier S, Oudard S, Gore ME, Tarazi J, Hariharan S, et al. Axitinib versus sorafenib as second-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma: overall survival analysis and updated results from a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:552–562. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70093-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
