Priming anti-tumor immunity by radiotherapy: Dying tumor cell-derived DAMPs trigger endothelial cell activation and recruitment of myeloid cells
- PMID: 30546963
- PMCID: PMC6287777
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2018.1523097
Priming anti-tumor immunity by radiotherapy: Dying tumor cell-derived DAMPs trigger endothelial cell activation and recruitment of myeloid cells
Abstract
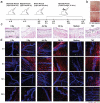
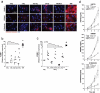
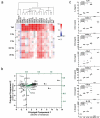
The major goal of radiotherapy is the induction of tumor cell death. Additionally, radiotherapy can function as in situ cancer vaccination by exposing tumor antigens and providing adjuvants for anti-tumor immune priming. In this regard, the mode of tumor cell death and the repertoire of released damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) are crucial. However, optimal dosing and fractionation of radiotherapy remain controversial. Here, we examined the initial steps of anti-tumor immune priming by different radiation regimens (20 Gy, 4 × 2 Gy, 2 Gy, 0 Gy) with cell lines of triple-negative breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. Previously, we have shown that especially high single doses (20 Gy) induce a delayed type of primary necrosis with characteristics of mitotic catastrophe and plasma membrane disintegration. Now, we provide evidence that protein DAMPs released by these dying cells stimulate sequential recruitment of neutrophils and monocytes in vivo. Key players in this regard appear to be endothelial cells revealing a distinct state of activation upon exposure to supernatants of irradiated tumor cells as characterized by high surface expression of adhesion molecules and production of a discrete cytokine/chemokine pattern. Furthermore, irradiated tumor cell-derived protein DAMPs enforced differentiation and maturation of dendritic cells as hallmarked by upregulation of co-stimulatory molecules and improved T cell-priming. Consistently, a recurring pattern was observed: The strongest effects were detected with 20 Gy-irradiated cells. Obviously, the initial steps of radiotherapy-induced anti-tumor immune priming are preferentially triggered by high single doses - at least in models of triple-negative breast cancer.
Keywords: APC recruitment; DAMPs; Radiotherapy; abscopal effects of radiotherapy; anti-tumor immunity; cancer immunotherapy; endothelial cell activation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Priming of Anti-tumor Immune Mechanisms by Radiotherapy Is Augmented by Inhibition of Heat Shock Protein 90.Front Oncol. 2020 Aug 27;10:1668. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01668. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32984042 Free PMC article.
-
Norm- and hypo-fractionated radiotherapy is capable of activating human dendritic cells.J Immunotoxicol. 2014 Oct;11(4):328-36. doi: 10.3109/1547691X.2014.880533. Epub 2014 Feb 10. J Immunotoxicol. 2014. PMID: 24512329
-
Combinations of Radiotherapy with Vaccination and Immune Checkpoint Inhibition Differently Affect Primary and Abscopal Tumor Growth and the Tumor Microenvironment.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 9;13(4):714. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040714. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33572437 Free PMC article.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors with radiotherapy and locoregional treatment: synergism and potential clinical implications.Curr Opin Oncol. 2015 Nov;27(6):445-51. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000000225. Curr Opin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26447875 Review.
-
The Effects of Gynecological Tumor Irradiation on the Immune System.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 9;16(16):2804. doi: 10.3390/cancers16162804. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199577 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of the Tumor Microenvironment in Developing Successful Therapeutic and Secondary Prophylactic Breast Cancer Vaccines.Vaccines (Basel). 2020 Sep 14;8(3):529. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8030529. Vaccines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32937885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential of damage associated molecular patterns in synergising radiation and the immune response in oesophageal cancer.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023 Aug 15;15(8):1349-1365. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i8.1349. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37663943 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and validation of a prognostic nine-gene signature associated with radiosensitivity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2023 Oct 2;43:100686. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2023.100686. eCollection 2023 Nov. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37854672 Free PMC article.
-
The use of RNA-based treatments in the field of cancer immunotherapy.Mol Cancer. 2023 Jul 7;22(1):106. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01807-w. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37420174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tracking cellular therapies to optimize homing against liver metastases.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 25;16:1611861. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1611861. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40636106 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
