Ameloblastoma: Management and Outcome
- PMID: 30546984
- PMCID: PMC6289562
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.3437
Ameloblastoma: Management and Outcome
Abstract
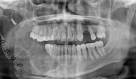
Introduction Ameloblastoma is a locally destructive tumor with a propensity for recurrence if not entirely excised. Management of ameloblastoma poses a challenge for all involved in the field of head and neck surgery because successful treatment requires not only adequate resection but also a functional and aesthetically acceptable reconstruction of the residual defect. Methods Patients who had histologically proven ameloblastoma between 1991 and 2009 were identified from the database of Aga Khan University Hospital. A review of all medical records, radiological images, operative reports and pathology reports was undertaken. Results A total of 15 patients with histologically confirmed ameloblastoma were identified. Out of 15 patients nine were males and six were females with age range from 20 to 60 years (mean age 43 years). The most common symptom found in our patient group was painless facial swelling. In 13 patients the origin of tumor was mandible and in the remaining two the tumor originated from maxilla. Eleven out of 15 patients underwent segmental mandibulectomy, two had maxillectomy and two had enucleation. All patients who underwent segmental mandibulectomy required reconstruction. Reconstruction was done with microsurgical free tissue transfer in eight patients, non-vascularized iliac crest bone graft was used in one patient and two had plating only. All free flaps survived with no evidence of flap loss. The mean follow-up was eight years. There was no evidence of graft failure which was used in one patient. Complication was seen in only one of our patients in the form of plate exposure. Recurrence was seen in two of our cases who primarily underwent enucleation. All patients had satisfactory speech, cosmesis and mastication. Conclusion The management of ameloblastoma still poses a big challenge in spite of being the most common odontogenic tumor. In our study we have found that segmental mandibulectomy with disease-free margin of around 1 cm and immediate reconstruction with free tissue transfer have shown good results.
Keywords: ameloblastoma; free fibular flap; multicystic ameloblastoma; odontogenic tumor; opg; orthopantomogram; solid ameloblastoma; tumors and cysts of jaw; unicystic ameloblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Ameloblastoma. Mendenhall WM, Werning JW, Fernandes R, Malyapa RS, Mendenhall NP. Am J Clin Oncol. 2007;30:645–648. - PubMed
-
- Ameloblastoma. Thompson LD. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/m/pubmed/12610896/ Ear Nose Throat J. 2003;82:19. - PubMed
-
- Frequency of odontogenic cysts and tumors: a systematic review. Johnson NR, Gannon OM, Savage NW, Batstone MD. J Investig Clin Dent. 2014;5:9–14. - PubMed
-
- Immediate mandibular reconstruction with microsurgical fibula flap transfer following wide resection for ameloblastoma. Gerzenshtein J, Zhang F, Caplan J, Anand V, Lineaweaver W. J Craniofac Surg. 2006;17:178–182. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
