Radiation-induced vascular malformations in the brain, mimicking tumor in MRI-based treatment response assessment maps (TRAMs)
- PMID: 30547098
- PMCID: PMC6282630
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ctro.2018.11.004
Radiation-induced vascular malformations in the brain, mimicking tumor in MRI-based treatment response assessment maps (TRAMs)
Abstract
•Of 310 brain tumors patients recruited, histology of 99 lesions was available.•Of those, 5 were histologically confirmed as radiation-induced malformations.•TRAMs cannot differentiate active tumor from vascular malformation.
Keywords: Brain tumors; MRI; RICM; RIT; Radiation; TRAMs; Vascular malformations.
Figures
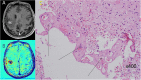
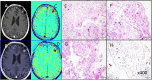
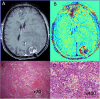
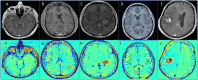
Similar articles
-
Delayed contrast extravasation MRI: a new paradigm in neuro-oncology.Neuro Oncol. 2015 Mar;17(3):457-65. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nou230. Epub 2014 Nov 30. Neuro Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25452395 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the diagnostic ability of treatment response assessment maps (TRAMs)/contrast clearance analysis (CCA) in predicting the presence of active brain tumors.Neuroradiol J. 2025 Feb 26:19714009251324305. doi: 10.1177/19714009251324305. Online ahead of print. Neuroradiol J. 2025. PMID: 40010303 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of radiation-induced cavernous malformations and comparison with a nonradiation cavernous malformation cohort.J Neurosurg. 2015 May;122(5):1214-22. doi: 10.3171/2015.1.JNS141452. Epub 2015 Feb 20. J Neurosurg. 2015. PMID: 25699412
-
Intracranial extra-axial cavernous (HEM) angiomas: tumors or vascular malformations?J Neuroradiol. 2002 Jun;29(2):91-104. J Neuroradiol. 2002. PMID: 12297731 Review.
-
[Classification of superficial vascular anomalies].Presse Med. 2010 Apr;39(4):457-64. doi: 10.1016/j.lpm.2009.07.029. Epub 2010 Mar 4. Presse Med. 2010. PMID: 20206462 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Delayed Contrast-enhanced MRI Distinguishes Tumor from Radiation Treatment Effect.Radiol Imaging Cancer. 2025 May;7(3):e240388. doi: 10.1148/rycan.240388. Radiol Imaging Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40214516 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Conventional and Advanced Imaging Techniques in Post-treatment Glioma Imaging.Front Radiol. 2022 Jun 28;2:883293. doi: 10.3389/fradi.2022.883293. eCollection 2022. Front Radiol. 2022. PMID: 37492665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MRI Treatment Response Assessment Maps (TRAMs) for differentiating recurrent glioblastoma from radiation necrosis.J Neurooncol. 2024 Feb;166(3):513-521. doi: 10.1007/s11060-024-04573-x. Epub 2024 Jan 23. J Neurooncol. 2024. PMID: 38261142
-
Non-Human Primates Receiving High-Dose Total-Body Irradiation are at Risk of Developing Cerebrovascular Injury Years Postirradiation.Radiat Res. 2020 Sep 16;194(3):277-287. doi: 10.1667/RADE-20-00051.1. Radiat Res. 2020. PMID: 32942304 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging of brain tumors in children: the basics-a narrative review.Transl Pediatr. 2021 Apr;10(4):1138-1168. doi: 10.21037/tp-20-285. Transl Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34012860 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brandsma D., Van Den Bent M.J. Pseudoprogression and pseudoresponse in the treatment of gliomas. Curr Opin Neurol. 2009;22(6):633–638. - PubMed
-
- Chamberlain M.C., Glantz M.J., Chalmers L., Van Horn A., Sloan A.E. Early necrosis following concurrent Temodar and radiotherapy in patients with glioblastoma. J Neurooncol. 2007;82(1):81–83. - PubMed
-
- De Wit M.C.Y., De Bruin H.G., Eijkenboom W., Sillevis Smitt P.A.E., Van Den Bent M.J. Immediate post-radiotherapy changes in malignant glioma can mimic tumor progression. Neurology. 2004;63(3):535–537. - PubMed
-
- Wang K.Y., Idowu O.R., Lin D.D.M. Radiology and imaging for cavernous malformations. Handb Clin Neurol. 2017;143:249–266. - PubMed
-
- Cutsforth-Gregory J.K., Lanzino G., Link M.J., Brown R.D. Characterization of radiation-induced cavernous malformations and comparison with a nonradiation cavernous malformation cohort. J Neurosurg. 2015;122(5):1214–1222. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

