Stroke in the Arab World: A bibliometric analysis of research activity (2002-2016)
- PMID: 30547100
- PMCID: PMC6276280
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ensci.2018.11.010
Stroke in the Arab World: A bibliometric analysis of research activity (2002-2016)
Abstract
Background: The Arab world has an increasing prevalence of strokes, a leading cause of death in this part of the world.
Aims: The aim of this article is to quantify the stroke research activity in the Arab countries over the past 15 years taking into consideration the population, GDP, and DALY of each country.
Methods: A PubMed search was conducted to find stroke research articles published from the Arab countries between 2002 and 2016 (inclusive). Medical subject headings related to strokes and author origin/affiliation were used for this purpose.
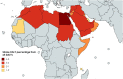
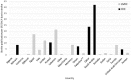
Results: The Arab world only produced 0.51% of all the stroke-related publications on PubMed even though the stroke-related DALY percentage in this region was greater than 2.88% during the period we studied. In general, the number of publications increased in the last few years. Somalia came first regarding the percentage of stroke to non-stroke publications released. Lebanon had the highest number of publications per GDP (in US Billion Dollars), Qatar had the highest number of publications per million persons (PPMP), while Saudi Arabia had the highest number of publications per 1% of stroke DALY. In addition, a strong positive correlation was found between the number of stroke publications and GDP; however, the correlation between the number of stroke publication and either population size or DALY was a weak positive one.
Conclusions: A general increase in publications is noticed, but stroke research activity in the Arab world is still poor compared to other parts of the world.
Keywords: Arab world; Bibliometric; DALY; GDP; Population; Stroke.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Insights in Neuropsychiatry: Suicide and Self-Mutilation in the Mena Region- a Bibliometric Quantitative and Co-occurrence Medline-Based Analysis.Cureus. 2021 Oct 11;13(10):e18680. doi: 10.7759/cureus.18680. eCollection 2021 Oct. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34786259 Free PMC article.
-
A Bibliometric Analysis of Neurosurgery Research Productivity in Arab Countries Between 2005 and 2019.World Neurosurg. 2021 Oct;154:e313-e319. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2021.07.026. Epub 2021 Jul 12. World Neurosurg. 2021. PMID: 34265430
-
Psoriasis: A bibliometric analysis in the Arab World (2004-2019).Australas J Dermatol. 2021 Feb;62(1):e19-e23. doi: 10.1111/ajd.13407. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Australas J Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 32757286
-
Rheumatology research output in the Arab World: despite the challenges.Reumatismo. 2022 Dec 29;74(3). doi: 10.4081/reumatismo.2022.1520. Reumatismo. 2022. PMID: 36580063 Review.
-
Nursing and midwifery research activity in Arab countries from 1950 to 2017.BMC Health Serv Res. 2019 May 28;19(1):340. doi: 10.1186/s12913-019-4178-y. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019. PMID: 31138250 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer research activity in the Arab world: a 15-year bibliometric analysis.J Egypt Public Health Assoc. 2022 Nov 17;97(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s42506-022-00120-6. J Egypt Public Health Assoc. 2022. PMID: 36385361 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with cognitive impairment at 3, 6, and 12 months after the first stroke among Lebanese survivors.Brain Behav. 2023 Jan;13(1):e2837. doi: 10.1002/brb3.2837. Epub 2022 Dec 10. Brain Behav. 2023. PMID: 36495111 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Leishmaniasis on the Performance of Elementary School Students: A Case Study among Syrian Refugees in Some Bekaa (Lebanon) Area Schools.J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2019 Dec;9(4):266-273. doi: 10.2991/jegh.k.190915.001. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2019. PMID: 31854168 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of Arab Countries to Familial Mediterranean Fever Research: a PubMed-based bibliometric analysis.Rheumatol Int. 2022 Jan;42(1):95-100. doi: 10.1007/s00296-021-04852-0. Epub 2021 Apr 12. Rheumatol Int. 2022. PMID: 33844039
-
Breast Cancer Epidemiology among Lebanese Women: An 11-Year Analysis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2019 Aug 10;55(8):463. doi: 10.3390/medicina55080463. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019. PMID: 31405167 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

