Treatment Decision-Making Involvement in Adolescents and Young Adults With Cancer
- PMID: 30547960
- PMCID: PMC7384435
- DOI: 10.1188/19.ONF.E22-E37
Treatment Decision-Making Involvement in Adolescents and Young Adults With Cancer
Abstract
Problem identification: Involvement in treatment decision making (TDM) is considered a key element of patient- and family-centered care and positively affects outcomes. However, for adolescents and young adults (AYAs) with cancer, little is known about the current state of knowledge about their perspective on and involvement in TDM or the factors influencing AYAs' TDM involvement.
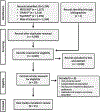
Literature search: Integrative review focused on AYAs aged 15-21 years, their involvement in TDM, and factors influencing their involvement using the MEDLINE®, PsycINFO®, CINAHL®, and Web of Science databases.
Data evaluation: 4,047 articles were identified; 21 met inclusion criteria.
Synthesis: Five factors were identified.
Implications for research: Research is needed to understand AYAs' preferences for TDM, the type and degree of their involvement, and the interactions between factors that contribute to or impede TDM.
Keywords: adolescent and young adult; decision making; patient participation; pediatric oncology.
Figures
References
-
- Albritton K, Caligiuri M, Anderson B, Nichols C, & Ulman D Adams H.,…Zebrack B. (2006). Closing the gap: Research and care imperatives for adolescents and young adults with cancer. Report of the Adolescent and Young Adult Oncology Progress Review Group. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.gov/types/aya/research/ayao-august-2006.pdf
-
- Barakat LP, Schwartz LA, Reilly A, Deatrick JA, & Balis F (2014). A qualitative study of phase III cancer clinical trial enrollment decision-making: Perspectives from adolescents, young adults, caregivers, and providers. Journal of Adolescent and Young Adult Oncology, 3, 3–11. 10.1089/jayao.2013.0011 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous