Lymphatic Vessel Network Structure and Physiology
- PMID: 30549020
- PMCID: PMC6459625
- DOI: 10.1002/cphy.c180015
Lymphatic Vessel Network Structure and Physiology
Abstract
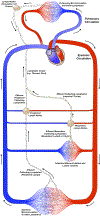
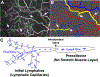
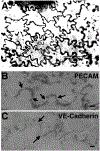
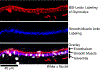
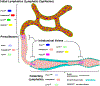
The lymphatic system is comprised of a network of vessels interrelated with lymphoid tissue, which has the holistic function to maintain the local physiologic environment for every cell in all tissues of the body. The lymphatic system maintains extracellular fluid homeostasis favorable for optimal tissue function, removing substances that arise due to metabolism or cell death, and optimizing immunity against bacteria, viruses, parasites, and other antigens. This article provides a comprehensive review of important findings over the past century along with recent advances in the understanding of the anatomy and physiology of lymphatic vessels, including tissue/organ specificity, development, mechanisms of lymph formation and transport, lymphangiogenesis, and the roles of lymphatics in disease. © 2019 American Physiological Society. Compr Physiol 9:207-299, 2019.
Copyright © 2019 American Physiological Society. All rights reserved.
Figures




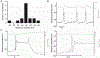
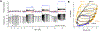
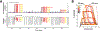
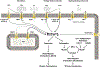
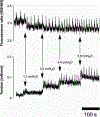
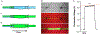
References
-
- Aagaard OC. Les vaisseaux lymphatiques du coeur chez l'homme et chez quelques mammifères. Copenhagen: Levin & Munksgaard, 1924.
-
- Aagaard OC. Über die Lymphgefässe der Zunge, des quergestreiften Muskelgewebes und der Speicheldrüsen des Menschen. Anatomische Hefte 47: 493–648, 1913.
-
- Abadie V, Badell E, Douillard P, Ensergueix D, Leenen PJ, Tanguy M, Fiette L, Saeland S, Gicquel B, and Winter N. Neutrophils rapidly migrate via lymphatics after Mycobacterium bovis BCG intradermal vaccination and shuttle live bacilli to the draining lymph nodes. Blood 106: 1843–1850, 2005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

