Successful Anti-PD-1 Cancer Immunotherapy Requires T Cell-Dendritic Cell Crosstalk Involving the Cytokines IFN-γ and IL-12
- PMID: 30552023
- PMCID: PMC6301092
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.09.024
Successful Anti-PD-1 Cancer Immunotherapy Requires T Cell-Dendritic Cell Crosstalk Involving the Cytokines IFN-γ and IL-12
Erratum in
-
Successful Anti-PD-1 Cancer Immunotherapy Requires T Cell-Dendritic Cell Crosstalk Involving the Cytokines IFN-γ and IL-12.Immunity. 2022 Sep 13;55(9):1749. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.07.021. Immunity. 2022. PMID: 36103861 No abstract available.
Abstract
Anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint blockers can induce sustained clinical responses in cancer but how they function in vivo remains incompletely understood. Here, we combined intravital real-time imaging with single-cell RNA sequencing analysis and mouse models to uncover anti-PD-1 pharmacodynamics directly within tumors. We showed that effective antitumor responses required a subset of tumor-infiltrating dendritic cells (DCs), which produced interleukin 12 (IL-12). These DCs did not bind anti-PD-1 but produced IL-12 upon sensing interferon γ (IFN-γ) that was released from neighboring T cells. In turn, DC-derived IL-12 stimulated antitumor T cell immunity. These findings suggest that full-fledged activation of antitumor T cells by anti-PD-1 is not direct, but rather involves T cell:DC crosstalk and is licensed by IFN-γ and IL-12. Furthermore, we found that activating the non-canonical NF-κB transcription factor pathway amplified IL-12-producing DCs and sensitized tumors to anti-PD-1 treatment, suggesting a therapeutic strategy to improve responses to checkpoint blockade.
Keywords: IFN-γ; IL-12; anti-PD-1; cancer; checkpoint; dendritic cell; immunotherapy; non-canonical NF-κB.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



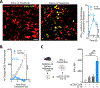
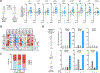
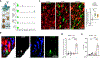
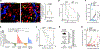
Comment in
-
The Dendritic Cell Strikes Back.Immunity. 2018 Dec 18;49(6):997-999. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.12.007. Immunity. 2018. PMID: 30566889
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R33 CA202064/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA101942/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 CA196035/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA206997/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA206890/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI056299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA224348/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI084880/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA079443/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK043351/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA218579/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI123349/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

