Co-repressor, co-activator and general transcription factor: the many faces of the Sin3 histone deacetylase (HDAC) complex
- PMID: 30552170
- PMCID: PMC6295471
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20170314
Co-repressor, co-activator and general transcription factor: the many faces of the Sin3 histone deacetylase (HDAC) complex
Abstract
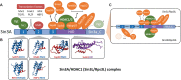
At face value, the Sin3 histone deacetylase (HDAC) complex appears to be a prototypical co-repressor complex, that is, a multi-protein complex recruited to chromatin by DNA bound repressor proteins to facilitate local histone deacetylation and transcriptional repression. While this is almost certainly part of its role, Sin3 stubbornly refuses to be pigeon-holed in quite this way. Genome-wide mapping studies have found that Sin3 localises predominantly to the promoters of actively transcribed genes. While Sin3 knockout studies in various species result in a combination of both up- and down-regulated genes. Furthermore, genes such as the stem cell factor, Nanog, are dependent on the direct association of Sin3 for active transcription to occur. Sin3 appears to have properties of a co-repressor, co-activator and general transcription factor, and has thus been termed a co-regulator complex. Through a series of unique domains, Sin3 is able to assemble HDAC1/2, chromatin adaptors and transcription factors in a series of functionally and compositionally distinct complexes to modify chromatin at both gene-specific and global levels. Unsurprisingly, therefore, Sin3/HDAC1 have been implicated in the regulation of numerous cellular processes, including mammalian development, maintenance of pluripotency, cell cycle regulation and diseases such as cancer.
Keywords: chromatin; deacetylase; histone; transcription.
© 2018 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

