Loss of Adult 5-HT1A Autoreceptors Results in a Paradoxical Anxiogenic Response to Antidepressant Treatment
- PMID: 30552180
- PMCID: PMC6381250
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0352-18.2018
Loss of Adult 5-HT1A Autoreceptors Results in a Paradoxical Anxiogenic Response to Antidepressant Treatment
Abstract
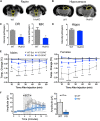
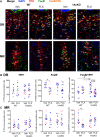
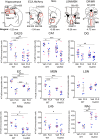
Selective serotonin (5-HT) reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are first-line antidepressants but require several weeks to elicit their actions. Chronic SSRI treatment induces desensitization of 5-HT1A autoreceptors to enhance 5-HT neurotransmission. Mice (both sexes) with gene deletion of 5-HT1A autoreceptors in adult 5-HT neurons (1AcKO) were tested for response to SSRIs. Tamoxifen-induced recombination in adult 1AcKO mice specifically reduced 5-HT1A autoreceptor levels. The 1AcKO mice showed a loss of 5-HT1A autoreceptor-mediated hypothermia and electrophysiological responses, but no changes in anxiety- or depression-like behavior. Subchronic fluoxetine (FLX) treatment induced an unexpected anxiogenic effect in 1AcKO mice in the novelty suppressed feeding and elevated plus maze tests, as did escitalopram in the novelty suppressed feeding test. No effect was seen in wild-type (WT) mice. Subchronic FLX increased 5-HT metabolism in prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, and raphe of 1AcKO but not WT mice, suggesting hyperactivation of 5-HT release. To detect chronic cellular activation, FosB+ cells were quantified. FosB+ cells were reduced in entorhinal cortex and hippocampus (CA2/3) and increased in dorsal raphe 5-HT cells of 1AcKO mice, suggesting increased raphe activation. In WT but not 1AcKO mice, FLX reduced FosB+ cells in the median raphe, hippocampus, entorhinal cortex, and median septum, which receive rich 5-HT projections. Thus, in the absence of 5-HT1A autoreceptors, SSRIs induce a paradoxical anxiogenic response. This may involve imbalance in activation of dorsal and median raphe to regulate septohippocampal or fimbria-fornix pathways. These results suggest that markedly reduced 5-HT1A autoreceptors may provide a marker for aberrant response to SSRI treatment.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Serotonin-selective reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are effective in treating anxiety and depression in humans and mouse models. However, in some cases, SSRIs can increase anxiety, but the mechanisms involved are unclear. Here we show that, rather than enhancing SSRI benefits, adulthood knockout (KO) of the 5-HT1A autoreceptor, a critical negative regulator of 5-HT activity, results in an SSRI-induced anxiety effect that appears to involve a hyperactivation of the 5-HT system in certain brain areas. Thus, subjects with very low levels of 5-HT1A autoreceptors, such as during childhood or adolescence, may be at risk for an SSRI-induced anxiety response.
Keywords: 5-HT1A receptor; anxiety; autoreceptor; knock-out; raphe; serotonin.
Copyright © 2019 the authors 0270-6474/19/391334-13$15.00/0.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
