Drug and disease signature integration identifies synergistic combinations in glioblastoma
- PMID: 30552330
- PMCID: PMC6294341
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-07659-z
Drug and disease signature integration identifies synergistic combinations in glioblastoma
Abstract
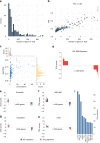
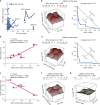
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common primary adult brain tumor. Despite extensive efforts, the median survival for GBM patients is approximately 14 months. GBM therapy could benefit greatly from patient-specific targeted therapies that maximize treatment efficacy. Here we report a platform termed SynergySeq to identify drug combinations for the treatment of GBM by integrating information from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and the Library of Integrated Network-Based Cellular Signatures (LINCS). We identify differentially expressed genes in GBM samples and devise a consensus gene expression signature for each compound using LINCS L1000 transcriptional profiling data. The SynergySeq platform computes disease discordance and drug concordance to identify combinations of FDA-approved drugs that induce a synergistic response in GBM. Collectively, our studies demonstrate that combining disease-specific gene expression signatures with LINCS small molecule perturbagen-response signatures can identify preclinical combinations for GBM, which can potentially be tested in humans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Comment in
-
Treatment Synergy for Glioblastoma Multiforme with SynergySeq.Neurosurgery. 2019 Aug 1;85(2):E178-E179. doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyz030. Neurosurgery. 2019. PMID: 30809656 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

