Innate T cells in the intensive care unit
- PMID: 30554082
- PMCID: PMC6331274
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2018.09.026
Innate T cells in the intensive care unit
Abstract
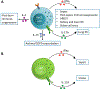
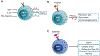
Rapid onset of acute inflammation is a hallmark of critical illnesses that bring patients to the intensive care unit (ICU). In critical illness, innate T cells rapidly reach full activation and drive a robust acute inflammatory response. As "cellular adjuvants," innate T cells worsen inflammation and mortality in several common critical illnesses including sepsis, ischemia-reperfusion injury, stroke, and exacerbations of respiratory disease. Interestingly, innate T cell subsets can also promote a protective and anti-inflammatory response in sepsis, ischemia-reperfusion injury, and asthma. Therapies that target innate T cells have been validated in several models of critical illness. Here, we review the role of natural killer T (NKT) cells, mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells and γδ T cells in clinical and experimental critical illness.
Keywords: Cardiac arrest; Critical care; Gamma delta T cell; MAIT cell; NKT cell; Sepsis.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Aoyagi T, Yamamoto N, Hatta M, Tanno D, Miyazato A, Ishii K, Suzuki K, Nakayama T, Taniguchi M, Kunishima H, Hirakata Y, Kaku M, Kawakami K, 2011. Activation of pulmonary invariant NKT cells leads to exacerbation of acute lung injury caused by LPS through local production of IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha by Gr-1+ monocytes. Int Immunol 23, 97–108. 10.1093/intimm/dxq460 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

