Metformin Affects Heme Function as a Possible Mechanism of Action
- PMID: 30554148
- PMCID: PMC6385989
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.118.200803
Metformin Affects Heme Function as a Possible Mechanism of Action
Abstract
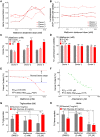
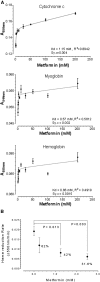
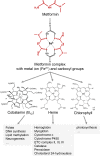
Metformin elicits pleiotropic effects that are beneficial for treating diabetes, as well as particular cancers and aging. In spite of its importance, a convincing and unifying mechanism to explain how metformin operates is lacking. Here we describe investigations into the mechanism of metformin action through heme and hemoprotein(s). Metformin suppresses heme production by 50% in yeast, and this suppression requires mitochondria function, which is necessary for heme synthesis. At high concentrations comparable to those in the clinic, metformin also suppresses heme production in human erythrocytes, erythropoietic cells and hepatocytes by 30-50%; the heme-targeting drug artemisinin operates at a greater potency. Significantly, metformin prevents oxidation of heme in three protein scaffolds, cytochrome c, myoglobin and hemoglobin, with Kd values < 3 mM suggesting a dual oxidation and reduction role in the regulation of heme redox transition. Since heme- and porphyrin-like groups operate in diverse enzymes that control important metabolic processes, we suggest that metformin acts, at least in part, through stabilizing appropriate redox states in heme and other porphyrin-containing groups to control cellular metabolism.
Keywords: diabetes; heme; hemoprotein; mechanism of action; metformin; porphyrin; redox.
Copyright © 2019 Li et al.
Figures

References
-
- Abu-el-wafa S. M., El-ries M. A., Ahmed F. H., 1987. Formation of Metformin Complexes with Some Transition-Metal Ions - Their Biological-Activity. Inorganica Chimica Acta-Bioinorganic Chemistry 136: 127–131. 10.1016/S0020-1693(00)81143-3 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
