Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis of Human Lung Provides Insights into the Pathobiology of Pulmonary Fibrosis
- PMID: 30554520
- PMCID: PMC6580683
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201712-2410OC
Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis of Human Lung Provides Insights into the Pathobiology of Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
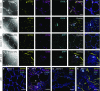
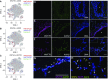
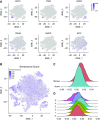
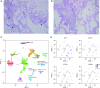
Rationale: The contributions of diverse cell populations in the human lung to pulmonary fibrosis pathogenesis are poorly understood. Single-cell RNA sequencing can reveal changes within individual cell populations during pulmonary fibrosis that are important for disease pathogenesis. Objectives: To determine whether single-cell RNA sequencing can reveal disease-related heterogeneity within alveolar macrophages, epithelial cells, or other cell types in lung tissue from subjects with pulmonary fibrosis compared with control subjects. Methods: We performed single-cell RNA sequencing on lung tissue obtained from eight transplant donors and eight recipients with pulmonary fibrosis and on one bronchoscopic cryobiospy sample from a patient with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. We validated these data using in situ RNA hybridization, immunohistochemistry, and bulk RNA-sequencing on flow-sorted cells from 22 additional subjects. Measurements and Main Results: We identified a distinct, novel population of profibrotic alveolar macrophages exclusively in patients with fibrosis. Within epithelial cells, the expression of genes involved in Wnt secretion and response was restricted to nonoverlapping cells. We identified rare cell populations including airway stem cells and senescent cells emerging during pulmonary fibrosis. We developed a web-based tool to explore these data. Conclusions: We generated a single-cell atlas of pulmonary fibrosis. Using this atlas, we demonstrated heterogeneity within alveolar macrophages and epithelial cells from subjects with pulmonary fibrosis. These results support the feasibility of discovery-based approaches using next-generation sequencing technologies to identify signaling pathways for targeting in the development of personalized therapies for patients with pulmonary fibrosis.
Keywords: RNA sequencing; alveolar macrophages; alveolar type II cells; pulmonary fibrosis.
Figures
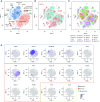
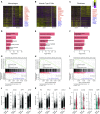

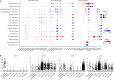
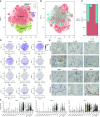

Comment in
-
Defining the Cell Types That Drive Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Using Single-Cell RNA Sequencing.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Jun 15;199(12):1454-1456. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201901-0197ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019. PMID: 30715901 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lederer DJ, Martinez FJ. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1811–1823. - PubMed
-
- Hutchinson J, Fogarty A, Hubbard R, McKeever T. Global incidence and mortality of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a systematic review. Eur Respir J. 2015;46:795–806. - PubMed
-
- Collard HR, Chen SY, Yeh WS, Li Q, Lee YC, Wang A, et al. Health care utilization and costs of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in US Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 years and older. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015;12:981–987. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- I01 CX001777/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- K08 HL125940/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD011996/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI135964/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL125910/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001422/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES015024/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067687/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134375/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL085534/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134800/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL076139/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES013995/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL048129/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- L30 HL134087/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HL119995/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL048129/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AR066579/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 ES025644/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 HL127245/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX000201/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- K08 HL128867/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL143135/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG049665/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL071643/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR064546/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI126031/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL128194/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD010398/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL136111/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 HL135124/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

