Characterization of a new exopolysaccharide produced by Halorubrum sp. TBZ112 and evaluation of its anti-proliferative effect on gastric cancer cells
- PMID: 30555767
- PMCID: PMC6281538
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-018-1515-5
Characterization of a new exopolysaccharide produced by Halorubrum sp. TBZ112 and evaluation of its anti-proliferative effect on gastric cancer cells
Abstract
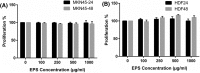
In the present study, we aimed to extract, purify, analyze monosaccharide composition of exopolysaccharide (EPS) produced by Halorubrum sp. TBZ112 (KCTC 4203 and IBRC-M 10773) and also to evaluate its possible antiproliferative activity against human gastric cancer (MKN-45) cell line and its biocompatibility effect on normal cells using human dermal fibroblast (HDF) cell line. Average molecular weight and monosaccharide composition were determined by high-pressure size exclusion chromatography (HPSEC) with multi-angle laser light scattering (MALLS) and high-pressure anion exchange chromatography (HPAEC), respectively. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy was used for the partial characterization of the EPS. The EPS effect on the cell proliferation and viability of MKN-45 and HDF cells was assessed using 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay and trypan blue dye exclusion, respectively. Strain TBZ112 excreted 480 mg.l-1 of the EPS under optimal growth conditions. The EPS had a molecular weight of 5.052 kDa and was a heteropolysaccharide containing ten moieties mainly composed of mannose (19.95%), glucosamine (15.55%), galacturonic acid (15.43%), arabinose (12.24%), and glucuronic acid (12.05%). No significant difference of the EPS treatments on the proliferation activity of MKN-45 and HDF cells were observed (P > 0.05). For the first time, the EPS from Halorubrum sp. TBZ112, an extremely halophilic archaeon related to Halorubrum genus, was isolated and chemically characterized. The EPS from Halorubrum sp. TBZ112 possesses a relatively low molecular weight and might be applied as a biocompatible compound. More investigations are needed to determine other biological activities of the EPS along with further details of its chemical structure.
Keywords: Antiproliferative effect; Exopolysaccharide (EPS); Halorubrum sp. TBZ112; Monosaccharide composition.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standardsThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional and cell proliferative properties of an exopolysaccharide produced by Nitratireductor sp. PRIM-31.Int J Biol Macromol. 2016 Apr;85:400-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.12.091. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016. PMID: 26772917
-
Preparation and Bioactivity of Exopolysaccharide from an Endophytic Fungus Chaetomium sp. of the Medicinal Plant Gynostemma Pentaphylla.Pharmacogn Mag. 2017 Jul-Sep;13(51):477-482. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.211033. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Pharmacogn Mag. 2017. PMID: 28839375 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization, structural characterization, and biological applications of exopolysaccharide produced by Enterococcus faecium KT990028.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Dec;282(Pt 4):136926. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.136926. Epub 2024 Oct 31. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39486715
-
Modification of exopolysaccharide composition and production by three cyanobacterial isolates under salt stress.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2010 Mar;17(3):595-602. doi: 10.1007/s11356-009-0233-2. Epub 2009 Sep 1. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2010. PMID: 19727881
-
Modeling and Optimum Extraction of Multiple Bioactive Exopolysaccharide from an Endophytic Fungus of Crocus sativus L.Pharmacogn Mag. 2018 Jan-Mar;14(53):36-43. doi: 10.4103/pm.pm_96_17. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Pharmacogn Mag. 2018. PMID: 29576699 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exopolysaccharide composition and size in Sulfolobus acidocaldarius biofilms.Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 26;13:982745. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.982745. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36225367 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Robust Microbiota Signatures and Interpretable Rules to Distinguish Cancer Subtypes.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Nov 4;7:604794. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.604794. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33330634 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and Prospective Applications of the Exopolysaccharides Produced by Rhodosporidium babjevae.Adv Pharm Bull. 2020 Jun;10(2):254-263. doi: 10.34172/apb.2020.030. Epub 2020 Feb 18. Adv Pharm Bull. 2020. PMID: 32373494 Free PMC article.
-
Halophiles and Their Biomolecules: Recent Advances and Future Applications in Biomedicine.Mar Drugs. 2019 Dec 30;18(1):33. doi: 10.3390/md18010033. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31906001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytotoxic effects of halophilic archaea metabolites on ovarian cancer cell lines.Microb Cell Fact. 2023 Sep 28;22(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s12934-023-02206-y. Microb Cell Fact. 2023. PMID: 37759261 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

