The CryoEM Method MicroED as a Powerful Tool for Small Molecule Structure Determination
- PMID: 30555912
- PMCID: PMC6276044
- DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.8b00760
The CryoEM Method MicroED as a Powerful Tool for Small Molecule Structure Determination
Abstract
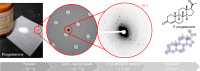
In the many scientific endeavors that are driven by organic chemistry, unambiguous identification of small molecules is of paramount importance. Over the past 50 years, NMR and other powerful spectroscopic techniques have been developed to address this challenge. While almost all of these techniques rely on inference of connectivity, the unambiguous determination of a small molecule's structure requires X-ray and/or neutron diffraction studies. In practice, however, X-ray crystallography is rarely applied in routine organic chemistry due to intrinsic limitations of both the analytes and the technique. Here we report the use of the electron cryo-microscopy (cryoEM) method microcrystal electron diffraction (MicroED) to provide routine and unambiguous structural determination of small organic molecules. From simple powders, with minimal sample preparation, we could collect high-quality MicroED data from nanocrystals (∼100 nm, ∼10-15 g) resulting in atomic resolution (<1 Å) crystal structures in minutes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
Tiny crystals have big potential for determining structures of small molecules.Nature. 2018 Dec;564(7736):348-349. doi: 10.1038/d41586-018-07756-5. Nature. 2018. PMID: 30559356 No abstract available.
References
-
- Schreier P.; Bernreuther A.; Huffer M.. Analysis of Chiral Organic Molecules: Methodology and Applications; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, 2011.
-
- Scott A. I.Interpretation of the Ultraviolet Spectra of Natural Products: International Series of Monographs on Organic Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, 2013; Vol. 7.
-
- Coates J.Interpretation of infrared spectra, a practical approach. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry: Applications, Theory and Instrumentation; Meyers R. A., Ed.; Wiley: New York, 2000; Vol. 12, pp 10815–10837.
-
- Dougherty D. A. Spin control in organic molecules. Acc. Chem. Res. 1991, 24, 88–94. 10.1021/ar00003a005. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

