Identification of pathogenic YY1AP1 splice variants in siblings with Grange syndrome by whole exome sequencing
- PMID: 30556293
- PMCID: PMC6590215
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.a.60700
Identification of pathogenic YY1AP1 splice variants in siblings with Grange syndrome by whole exome sequencing
Abstract
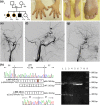
Grange syndrome is an autosomal recessive condition characterized by arterial occlusions and hypertension. Syndactyly, brachydactyly, bone fragility, heart defects, and learning disabilities have also been reported. Loss-of-function variants in YY1AP1 have only recently been associated with Grange syndrome. YY1AP1 encodes for the transcription coactivator yin yang 1-associated protein 1 which regulates smooth muscle cell proliferation and differentiation. We here report on three siblings with steno-occlusive arterial disorder and syndactyly in two of them. Whole exome sequencing including near-splice regions led to the identification of two intronic YY1AP1 variants which were predicted to interfere with normal splicing. Sanger sequencing demonstrated compound-heterozygosity in all affected siblings. RT-PCR analyses confirmed skipping of exon 6 on one allele and exonization of 22 bp in intron 6 on the other. This is the first report of biallelic YY1AP1 variants in noncoding regions and just the second family with multiple affected siblings. Therefore, our report further delineates the phenotypic spectrum of Grange syndrome.
Keywords: Grange syndrome; splice variant; vascular disease; whole exome sequencing.
© 2018 The Authors. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures
References
-
- Baradhi, K. M. , & Bream, P. (2018). Fibromuscular Dysplasia. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL). StatPearls Publishing. Retrieved from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493204/. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29630256. - PubMed
-
- Grange, D. K. , Balfour, I. C. , Chen, S. C. , & Wood, E. G. (1998). Familial syndrome of progressive arterial occlusive disease consistent with fibromuscular dysplasia, hypertension, congenital cardiac defects, bone fragility, brachysyndactyly, and learning disabilities. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 75(5), 469–480. - PubMed
-
- Guo, D. C. , Duan, X. Y. , Regalado, E. S. , Mellor‐Crummey, L. , Kwartler, C. S. , Kim, D. , … Milewicz, D. M. (2017). Loss‐of‐function mutations in YY1AP1 Lead to Grange syndrome and a fibromuscular dysplasia‐like vascular disease. American Journal of Human Genetics, 100(1), 21–30. 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.11.008 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rath, M. , Korenke, G. C. , Najm, J. , Hoffmann, G. F. , Hagendorff, A. , Strom, T. M. , & Felbor, U. (2017). Exome sequencing results in identification and treatment of brain dopamine‐serotonin vesicular transport disease. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 379, 296–297. 10.1016/j.jns.2017.06.034 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

