Cholinesterase inhibitor rivastigmine enhances nerve growth factor-induced neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells via sigma-1 and sigma-2 receptors
- PMID: 30557385
- PMCID: PMC6296549
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209250
Cholinesterase inhibitor rivastigmine enhances nerve growth factor-induced neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells via sigma-1 and sigma-2 receptors
Abstract
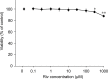
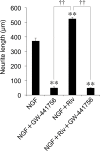
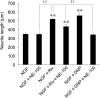
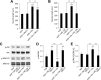
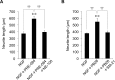
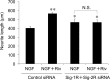
Rivastigmine (Riv) is a potent and selective cholinesterase (acetylcholinesterase, AChE and butyrylcholinesterase, BuChE) inhibitor developed for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD). To elucidate whether Riv causes neuronal differentiation, we examined its effect on nerve growth factor (NGF)-induced neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells. At concentrations of 0-100 μM, Riv was non-toxic in PC12 cells. Riv caused dose-dependent (10-100 μM) enhancement of NGF-induced neurite outgrowth, which was completely inhibited by the TrkA antagonist GW-441756. By contrast, Riv-mediated enhancement of neurite outgrowth was not blocked by the acetylcholine receptor antagonists, scopolamine and hexamethonium. However, the sigma-1 receptor (Sig-1R) antagonist NE-100 and sigma-2 receptor (Sig-2R) antagonist SM-21 each blocked about half of the Riv-mediated enhancement of NGF-induced neurite outgrowth. Interestingly, the simultaneous application of NE-100 and SM-21 completely blocked the enhancement of NGF-induced neurite outgrowth by Riv. These findings suggest that both Sig-1R and Sig-2R play important roles in NGF-induced neurite outgrowth through TrkA and that Riv may contribute to neuronal repair via Sig-1R and Sig-2R in AD therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology 34: 939–944. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe DJ (2001) Alzheimer's disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev 81: 741–766. 10.1152/physrev.2001.81.2.741 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kasa P, Rakonczay Z, Gulya K (1997) The cholinergic system in Alzheimer's disease. Prog Neurobiol 52: 511–535. - PubMed
-
- Auld DS, Kornecook TJ, Bastianetto S, Quirion R (2002) Alzheimer's disease and the basal forebrain cholinergic system: relations to beta-amyloid peptides, cognition, and treatment strategies. Prog Neurobiol 68: 209–245. - PubMed
-
- Anand P, Singh B (2013) A review on cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease. Arch Pharm Res 36: 375–399. 10.1007/s12272-013-0036-3 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

