The paroxysmal depolarization shift in epilepsy research
- PMID: 30557621
- PMCID: PMC7116775
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2018.12.006
The paroxysmal depolarization shift in epilepsy research
Abstract
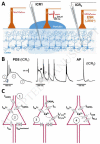
Several shortcomings with currently available pharmacotherapy of epilepsy necessitate the search for new drug targets. Paroxysmal depolarization shifts (PDS) represent the cellular correlates of electrographic (e.g. interictal) spikes. While the ionic basis of PDS is understood in great detail, controversy exists regarding their proposed implication in epilepsy. To address this issue and to consider potential targetability, this mini-review gives an overview of the ionic conductances contributing to PDS and reflects on the hypotheses of their potential pro-epileptic (epileptogenic) and anti-epileptic roles.
Keywords: Epileptogenesis; Hippocampal neurons; Interictal spike; L-type voltage-gated calcium channels.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Akaishi T, Nakazawa K, Sato K, Saito H, Ohno Y, Ito Y. Hydrogen peroxide modulates whole cell Ca2+ currents through L-type channels in cultured rat dentate granule cells. Neurosci Lett. 2004;356:25–28. - PubMed
-
- Antoniadis A, Müller WE, Wollert U. Inhibition of GABA and benzodiazepine receptor binding by penicillins. Neurosci Lett. 1980;18:309–312. - PubMed
-
- Bingmann D, Speckmann EJ, Baker RE, Ruijter J, de Jong BM. Differential antiepileptic effects of the organic calcium antagonists verapamil and flunarizine in neurons of organotypic neocortical explants from newborn rats. Exp Brain Res. 1988;72:439–442. - PubMed
-
- Chen S, Su H, Yue C, Remy S, Royeck M, Sochivko D, Opitz T, Beck H, Yaari Y. An increase in persistent sodium current contributes to intrinsic neuronal bursting after status epilepticus. J Neurophysiol. 2011;105:117–129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

